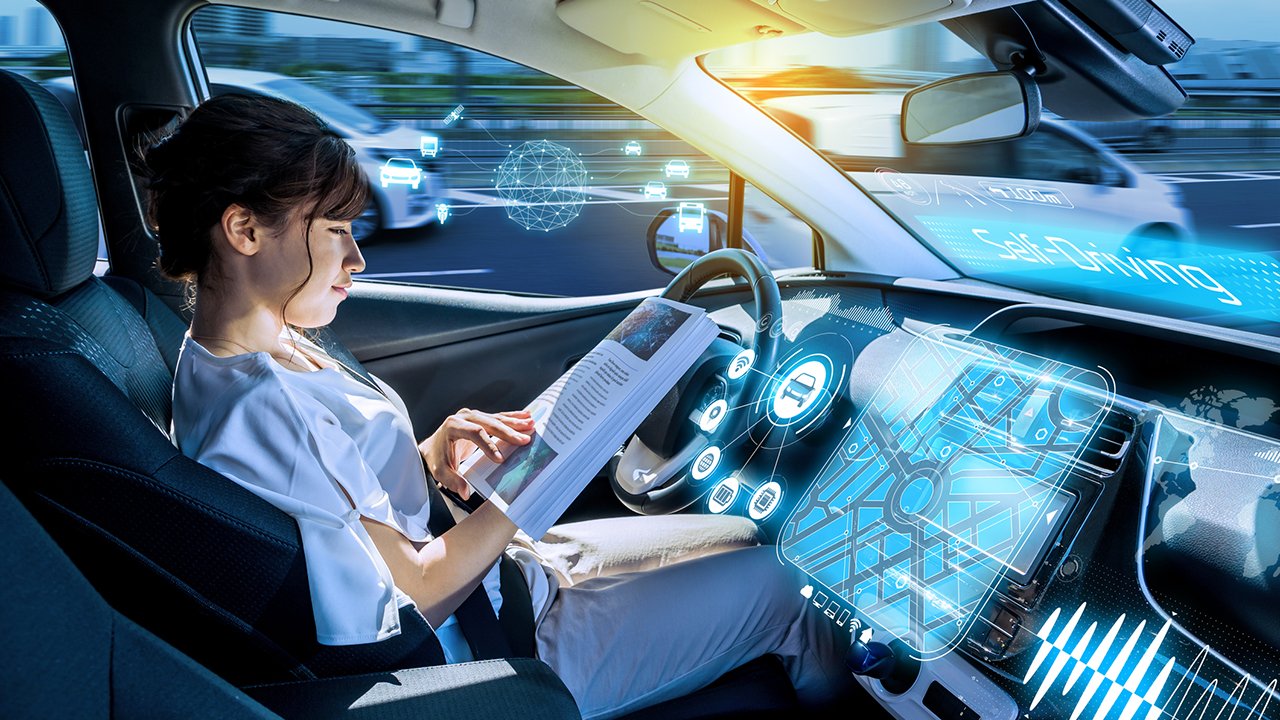

Smart Transportation
Introduction to 5G Technology
5G technology represents the fifth generation of mobile network advancements, set to revolutionize various industries with its remarkable attributes. Unlike its predecessors, 5G offers significantly higher speeds, enhanced reliability, and lower latency, making it a cornerstone for future technological developments, including smart transportation. These attributes collectively present a powerful infrastructure that supports the increasingly connected world.
One of the most notable improvements brought by 5G is its high-speed capabilities. With download speeds approaching up to 10 Gbps, 5G is substantially faster than 4G, enabling real-time data transmission. This speed improvement facilitates various high-bandwidth applications, such as ultra-high-definition video streaming, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR), which were previously constrained by slower networks.
Another critical feature of 5G technology is its remarkably low latency, typically around 1 millisecond. Latency, the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another, is crucial for applications requiring immediate feedback. This low latency is vital for the seamless operation of connected cars, where split-second decisions can significantly impact safety and efficiency.
Beyond speed and latency, 5G also boasts increased network capacity, capable of supporting a large number of devices simultaneously without compromising performance. This enhancement is particularly beneficial as the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices continues to grow exponentially. The ability to handle vast amounts of data traffic ensures that each connected device, including connected cars, can operate reliably and efficiently.
Reliability is another hallmark of 5G technology. With advanced error correction and robust signal strength, 5G networks can maintain continuous and stable connections. This reliability is essential for critical applications, such as autonomous driving and real-time traffic management, where consistent connectivity is required for optimal performance.
In summary, 5G technology offers exceptional improvements in speed, latency, capacity, and reliability. These features set the foundation for transformative advancements in numerous sectors, particularly in the realm of connected cars, promising a future of smart and efficient transportation.
The Evolution of Connected Cars
The journey of connected cars traces back decades, beginning with basic in-car internet access. Early models, equipped with rudimentary GPS navigation systems in the late 1990s and early 2000s, marked the initial steps towards vehicle connectivity. These systems laid the groundwork for more complex and integrated technologies that would follow.
As consumer demand for connectivity grew, so did advancements in automotive technology. The mid-2000s saw the introduction of systems like General Motors’ OnStar, which provided enhanced security and diagnostics features through satellite communication. This era marked significant progress because it enabled vehicles to communicate with external networks, offering drivers unprecedented convenience and safety features.
The advent of 4G LTE networks in the 2010s further accelerated the evolution of connected cars. Faster internet speeds and improved network reliability allowed for more sophisticated applications, ranging from real-time traffic updates to streaming media services within vehicles. Automakers began embedding SIM cards directly into the car’s central console, facilitating continual connectivity.
Most recent advancements have been driven by the development and implementation of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. This technology enables cars to interact not only with other vehicles but also infrastructure, pedestrians, and the broader internet ecosystem. V2X encompasses various communication types, including V2V (vehicle-to-vehicle), V2I (vehicle-to-infrastructure), and V2P (vehicle-to-pedestrian). These capabilities promise to enhance road safety, improve traffic management, and support autonomous driving functions.
Current market trends indicate rapid growth and adoption of connected car technologies. According to recent reports, the global connected car market is projected to reach over $200 billion by 2030. This momentum is driven by consumer expectations for smart features, regulatory pushes for improved safety measures, and ongoing innovations by tech companies and automakers alike.

Overall, the evolution of connected cars showcases a profound transformation in how vehicles operate and interact with their surroundings, setting the stage for a future where transportation is smarter, safer, and more efficient.
How 5G Will Transform Connected Vehicles
5G technology is set to revolutionize the landscape of connected cars by significantly enhancing various aspects of smart transportation. One of the most profound impacts will be on autonomous driving capabilities. With the ultra-low latency and high-speed connectivity of 5G, autonomous vehicles can process vast amounts of data in real-time. This enables quicker decision-making, reducing critical response times and making self-driving cars safer and more efficient than ever before. For instance, in complex traffic situations, real-time data processing allows for immediate adjustments to speed, route, and driving behavior, optimizing the overall flow of traffic.
Real-time communication between vehicles (Vehicle-to-Vehicle, or V2V) and with infrastructure (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure, or V2I) is another transformative aspect enabled by 5G. V2V communication allows cars to share information about speed, position, and road conditions directly with each other. This can prevent accidents by giving advanced warning of sudden braking or poor road conditions. V2I communication integrates vehicles with smart infrastructure, such as traffic lights, road sensors, and urban management systems. A use case could be a connected car receiving a signal from a traffic light to slow down due to an upcoming congestion, thereby promoting efficient urban traffic management and reducing emissions.
Enhanced navigation and safety features are also on the horizon with the advent of 5G. High-definition maps updated in real-time will provide precise routing, resulting in more efficient travel and fuel savings. Moreover, road safety is significantly improved with the integration of 5G. For example, vehicles equipped with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) can leverage real-time data to anticipate potential hazards and assist the driver in avoiding collisions.
The deployment of 5G in connected vehicles promises a future where autonomous driving, seamless vehicle communication, and advanced safety features converge to deliver a smarter, more connected, and safer transportation ecosystem.
Intersection of 5G and Autonomous Driving
The advent of 5G technology is poised to revolutionize the landscape of autonomous driving. The fusion of 5G’s low latency and high reliability with the capabilities of autonomous vehicles represents a significant leap forward for smart transportation systems. One of the most critical aspects of 5G technology is its ability to support real-time data processing and decision-making, which are paramount for the safe and efficient operation of autonomous vehicles.
Low latency is essential in autonomous driving as vehicles need to react instantaneously to dynamic road conditions and unforeseen obstacles. Traditional 4G networks, with their higher latency, do not offer the responsiveness required for real-time decision-making. In contrast, 5G networks, with latency as low as 1 millisecond, enable vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructure in near real-time. This immediacy ensures that autonomous cars can process volumes of data from sensors, cameras, and other sources promptly, facilitating precise and rapid responses.
High reliability is another cornerstone of 5G, crucial for the consistent performance expected from autonomous driving systems. The seamless connectivity offered by 5G ensures that data transmission remains uninterrupted, which is vital for the continuous functioning of autonomous vehicles. This consistency supports not just vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication but also vehicle-to-everything (V2X) interactions, including traffic signals, pedestrians, and cyclists, thereby creating a more integrated and safer transportation ecosystem.
Industry experts like Dr. John Smith, a leading researcher in autonomous vehicle technology, highlight that “5G’s capabilities are foundational for the maturation of autonomous driving.” Recent studies also reinforce this view, demonstrating that 5G can substantially reduce the potential for accidents by enabling more synchronized and predictive driving behaviors. Additionally, the increased bandwidth and network slicing capabilities of 5G allow for the segregation of critical autonomous driving functions from other less critical use cases, ensuring priority and reliability for essential operations.
In conclusion, the intersection of 5G and autonomous driving heralds a new era for smart transportation, promising safer, more efficient, and highly responsive autonomous vehicles. This synergy is not just a technological enhancement but also a fundamental shift towards sustainable and intelligent mobility solutions for the future.
Benefits for Consumers and Society
The advent of 5G-powered connected cars stands to revolutionize the transportation landscape, providing a multitude of benefits for both consumers and society. One of the most significant advantages is enhanced road safety. Equipped with advanced sensors and real-time data processing capabilities, these vehicles can communicate with each other and infrastructure, reducing the likelihood of accidents by predicting hazards and facilitating quicker response times.
5G technology also holds the promise of reducing traffic congestion. With vehicles connected to a unified network, traffic data can be analyzed and shared instantaneously, enabling better traffic management and more efficient routing. This can lead to smoother traffic flow, potentially reducing daily commute times and easing the stress associated with congested roads.
Improved fuel efficiency is another notable benefit. Connected cars driven by 5G can optimize their routes and driving patterns, which minimizes fuel consumption. This not only results in cost savings for consumers but also contributes positively to environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. More efficient driving systems can mitigate the adverse environmental impact of traditional vehicles and represent a step forward in combating climate change.
Additionally, the convenience of advanced infotainment systems cannot be overlooked. With high-speed 5G connectivity, passengers can enjoy uninterrupted streaming, seamless navigation, and access to a variety of in-car services. This elevates the overall driving experience, making long trips more enjoyable and productive.
Societal benefits are equally compelling. The widespread adoption of 5G-connected cars could reduce the financial burden on healthcare systems by lowering the number of road accidents and associated injuries. Moreover, the reduction in traffic congestion can lead to fewer emissions, benefiting public health by improving air quality.
In essence, the integration of 5G technology into connected cars heralds a future of smarter, safer, and more efficient transportation, enhancing the quality of life for consumers and fostering a more sustainable society.
Challenges and Barriers to Implementation
The transition to 5G-enabled connected car technology is fraught with several significant challenges and barriers that need to be addressed to achieve its full potential. One of the primary obstacles is infrastructure development. The widespread deployment of 5G networks requires substantial investment in new cell towers and antennae, especially in rural and less densely populated areas. Ensuring comprehensive network coverage is crucial for the seamless operation of connected cars, yet this necessitates a considerable financial commitment and collaboration among telecom companies, governments, and various stakeholders.
Cybersecurity and data privacy concerns present another layer of complexity. With connected cars generating and transmitting vast amounts of data, the risk of cyberattacks becomes a critical issue. Ensuring robust security measures and privacy protections is essential to prevent unauthorized access and misuse of sensitive information. This involves the development of advanced encryption technologies and stringent authentication protocols, which are still evolving to keep pace with the rapid advancements in 5G and connected vehicle technologies.
Regulatory and legal hurdles also pose significant challenges. The implementation of 5G and connected car systems operates within a highly regulated environment that varies significantly across regions. Standardization and harmonization of regulations are necessary to create a conducive environment for innovation and the smooth operation of connected vehicles across borders. Governments and regulatory bodies must work together to develop coherent policies that address issues such as liability in case of accidents and the sharing of spectrum resources.
The high costs associated with these technological advancements represent another critical barrier. From the costs associated with infrastructure deployment to the expenses related to developing and integrating advanced software and hardware components, the financial implications are substantial. To mitigate these costs, strategies such as public-private partnerships, subsidies, and financing models are being explored.
Ongoing efforts and solutions are being developed to address these challenges. Collaboration among industry leaders, researchers, and policymakers is essential to overcome these barriers. Innovations in cybersecurity, gradual regulatory advancements, and strategic investments are paving the way for the successful implementation of 5G in the realm of smart transportation.
Key Players and Innovations in the Industry
The 5G and connected car industry is a vibrant ecosystem shaped by prominent companies, organizations, and innovators dedicated to advancing smart transportation. Forefront in this domain are technology powerhouses such as Ericsson, Qualcomm, and Intel. These giants are paving the way, offering innovative 5G solutions that promise unparalleled connectivity and efficiency for autonomous vehicles.
Ericsson has been a crucial player in enhancing 5G’s role within connected cars, participating in numerous partnerships with automakers and network service providers to develop robust infrastructure. Their collaboration with Volvo, for instance, focuses on leveraging 5G for safer and more efficient vehicular communication systems.
Qualcomm, well-known for its advanced semiconductor solutions, has significantly contributed to the automotive sector through its Snapdragon Digital Chassis. This platform integrates key capabilities such as AI, connectivity, and cloud services to facilitate a seamless vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, enhancing vehicle safety and autonomous functionalities.
Intel, through its Mobileye subsidiary, is another trailblazer in the industry. Mobileye’s EyeQ chips, used in conjunction with 5G technology, offer high-performance processing required for autonomous driving. Collaborations with major manufacturers like BMW and Audi showcase Intel’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of vehicle autonomy and connectivity.
Beyond these tech giants, automotive manufacturers like Tesla, Ford, and General Motors (GM) are also pivotal in driving innovation in smart transportation. Tesla continues to lead with over-the-air software updates and full self-driving capabilities that rely on high-speed 5G networks. Ford’s recent partnership with Google aims to accelerate the deployment of data-driven business models using AI and machine learning facilitated by 5G connectivity.
Meanwhile, GM is making significant strides with its Ultium battery technology and Cruise autonomous vehicle division, relying heavily on 5G for real-time data processing and advanced navigation features. Innovative startups like Rivian and Zoox are equally important, introducing new paradigms in smart transportation with their electric and autonomous vehicle solutions.
Collectively, these key players and their cutting-edge innovations are set to redefine the landscape of smart transportation, bringing us closer to a future where connected cars and 5G technology harmoniously enhance mobility, safety, and operational efficiency on a global scale.
The Road Ahead: Future Prospects and Predictions
The integration of 5G technology with connected cars heralds a new era in smart transportation. As we look toward the future, several notable trends and technological advancements are on the horizon. One of the most anticipated developments is the enhancement of autonomous driving capabilities. The ultra-low latency and high-speed communication facilitated by 5G networks are set to significantly improve the real-time decision-making processes of autonomous vehicles. This, in turn, will pave the way for more widespread adoption of self-driving cars, potentially transforming urban mobility.
Another important aspect to consider is the interaction between connected cars and smart infrastructure. Future smart cities will likely feature interconnected traffic management systems, where 5G-enabled vehicles communicate with traffic lights, road signs, and even other vehicles to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. This interconnected ecosystem will enhance both safety and efficiency, ultimately reducing the environmental impact of transportation by minimizing idle times and fuel consumption.
Additionally, the evolution of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication will further solidify the role of 5G in smart transportation. V2X communication will enable cars to interact not only with traffic infrastructure but also with pedestrians and cyclists through mobile devices, enhancing situational awareness and preventing accidents. As this technology matures, we can expect a seamless integration of all road users into a cohesive system, promoting overall road safety.
On the consumer front, the rise of 5G will bring about a more personalized and connected driving experience. In-vehicle infotainment systems will benefit from high-speed internet, providing passengers with augmented reality dashboards, real-time navigation updates, and immersive entertainment options. Moreover, predictive maintenance, facilitated by the continuous flow of data between the vehicle and the manufacturer, will improve vehicle reliability and reduce unexpected breakdowns.
As we venture into this exciting future, it is imperative to address challenges such as data security and privacy. Ensuring that the vast amounts of data generated and shared by connected cars are protected will be crucial to maintaining public trust in these emerging technologies. Ongoing advancements in cybersecurity measures will likely play a key role in safeguarding the future of smart transportation.
Looking ahead, the synergy between 5G and connected cars promises to revolutionize the way we travel. With continuous innovation and investment, the landscape of smart transportation is set to become increasingly dynamic, efficient, and user-centric in the coming decade.






3 thoughts on “5G and the Connected Car: What the Future Holds for Smart Transportation”
Comments are closed.