
Introduction to Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets have become increasingly popular in recent years, primarily due to their potential health benefits and positive environmental impact. Unlike traditional diets that often include significant amounts of animal products, plant-based diets focus on consuming primarily fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. By emphasizing these nutrient-dense foods, individuals who follow a plant-based lifestyle can enjoy a variety of meals that are both satisfying and beneficial to their well-being.
One of the distinguishing features of plant-based diets is the significant reduction or complete avoidance of animal products such as meat, dairy, and eggs. Additionally, processed foods that are high in sugars, salts, and unhealthy fats are also minimized. By focusing on whole, unprocessed plant foods, individuals can benefit from a vast array of nutrients, including essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
Plant-based eating is not a one-size-fits-all approach and can encompass various dietary practices. Some individuals may choose to be completely vegan, excluding all animal products, while others might adopt a vegetarian diet that allows for dairy or eggs. Flexitarians primarily consume plant-based foods but occasionally include small amounts of animal products. These variations provide flexibility and make plant-based diets accessible to a broad range of people, regardless of their dietary preferences.
In terms of benefits, plant-based diets have been linked to numerous positive health outcomes, including improved heart health, better weight management, and lower risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and certain cancers. Furthermore, embracing a plant-based lifestyle can contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water, and decreasing deforestation related to animal agriculture. These advantages position plant-based diets as a compelling choice for those committed to enhancing personal health and protecting the environment.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Diets
The adoption of plant-based diets has been extensively linked to numerous health benefits, making it an increasingly popular choice among individuals seeking to improve their well-being. Research has shown that plant-based eating can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. A study published in the *Journal of the American Heart Association* found that individuals who followed a plant-based diet had a 16% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 32% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular conditions.
Beyond cardiovascular benefits, plant-based diets have been associated with better blood sugar management. According to a meta-analysis published in *Current Diabetes Reports*, plant-based dietary patterns are linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes and improved glycemic control in those who already have the disease. Such diets, rich in fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients, help maintain stable blood glucose levels and enhance insulin sensitivity.
Moreover, plant-based diets exert a protective effect against certain types of cancer. The *American Institute for Cancer Research* underscores that diets abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes contribute to a reduced risk of colorectal, prostate, and breast cancers. These foods contain vital components like fiber, vitamins, and phytochemicals, which play a crucial role in cancer prevention and overall cellular health.

In addition to physical health advantages, plant-based diets also foster mental well-being. A study in *Nutritional Neuroscience* highlights that individuals who consume a diet rich in plant-based foods experience lower rates of depression and anxiety. The abundance of micronutrients, omega-3 fatty acids, and anti-inflammatory compounds found in these foods helps support brain function and emotional health.
These compelling health benefits have been corroborated by real-life testimonials. For instance, Jane, a 45-year-old from California, reported dramatic improvements in her energy levels and a significant reduction in her cholesterol levels after transitioning to a plant-based diet. Such experiences, along with extensive scientific evidence, make a strong case for considering plant-based diets as a viable option for enhancing physical and mental health.
Environmental Impact of Animal Agriculture
The environmental impact of animal agriculture is multifaceted and far-reaching, contributing substantially to ecological degradation. One of the most significant factors is the emission of greenhouse gases. Livestock farming is a major source of methane and nitrous oxide, particularly through enteric fermentation in ruminants and manure management. These gases are far more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of their global warming potential, amplifying the urgency to address them.
Deforestation is another critical issue linked to animal agriculture. Vast expanses of tropical rainforests are cleared annually to create pasturelands and grow feed crops like soybeans. This deforestation not only leads to the loss of biodiversity but also disrupts carbon sequestration processes, exacerbating climate change. Forest conversion contributes to habitat destruction, putting countless species at risk of extinction.
Water contamination remains a pressing concern in areas with intensive animal farming practices. The runoff from livestock operations often contains high levels of nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, which lead to eutrophication in water bodies. This process causes harmful algal blooms, depleting oxygen levels in water and resulting in dead zones where aquatic life cannot survive. Furthermore, antibiotic and hormone residues from animal agriculture infiltrate water sources, posing risks to both human health and ecosystems.
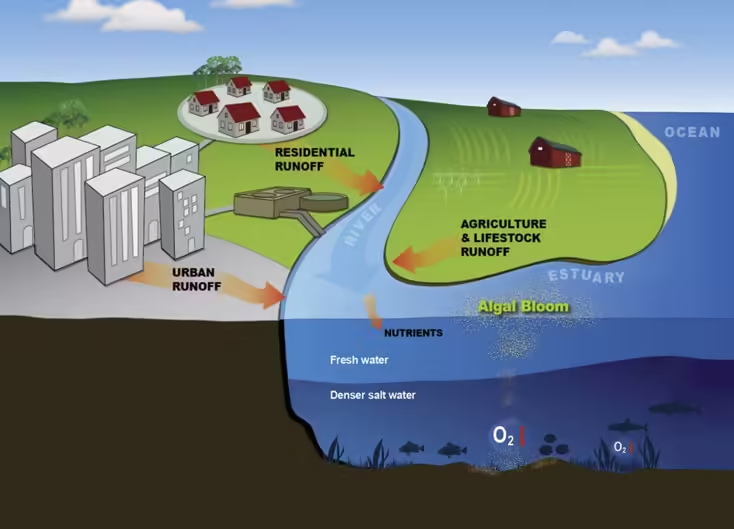
Resource depletion further underscores the unsustainability of current animal agriculture practices. The sector demands substantial quantities of water and feed. For example, producing one kilogram of beef requires an estimated 15,000 liters of water. In addition to water usage, land allocation is heavily skewed towards animal feed production rather than direct human consumption, reflecting inefficiencies in resource utilization.
Reducing the consumption of animal products can mitigate these environmental impacts significantly. By shifting towards plant-based diets, we can decrease greenhouse gas emissions, conserve vital forests, improve water quality, and optimize our use of natural resources. Embracing such dietary changes is not only a matter of personal health but also a critical step towards ensuring the sustainability of our planet.
The Role of Plant-Based Diets in Sustainability
Adopting a plant-based diet plays a significant role in promoting sustainability. One of the primary benefits is the substantial reduction in carbon footprint associated with plant-based eating. Animal agriculture is a leading driver of greenhouse gas emissions globally. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), livestock accounts for about 14.5% of global greenhouse emissions. By choosing plant-based foods, individuals can significantly lower their personal contribution to these emissions, fostering a more sustainable environment.
Water conservation is another critical aspect where plant-based diets have a significant impact. Producing plant-based foods generally requires less water compared to raising livestock. For instance, it takes approximately 1,800 gallons of water to produce a single pound of beef. In contrast, growing a pound of vegetables requires only about 39 gallons of water. Thus, shifting towards a diet rich in vegetables, grains, and legumes can lead to significant water savings, addressing freshwater scarcity issues that many regions face today.
Preserving biodiversity also forms a crucial argument for plant-based diets. Large-scale animal farming often leads to deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution, all of which threaten various species and ecosystems. The conversion of forests to farmland for livestock feed production particularly contributes to the loss of biodiversity. Conversely, plant-based agriculture, when managed responsibly, can coexist with natural ecosystems, allowing for the preservation and even enhancement of biodiversity.
Several studies and examples underscore these environmental benefits. A report by the University of Oxford found that cutting meat and dairy products from one’s diet could reduce an individual’s carbon footprint from food by up to 73%. Furthermore, initiatives like “Meatless Mondays” and the increasing popularity of plant-based products demonstrate how small changes in diet can collectively contribute to a more sustainable future.

In summary, the shift towards plant-based diets not only offers health benefits but also stands as a powerful step towards ensuring the sustainability of our planet. By reducing carbon emissions, conserving water, and protecting biodiversity, plant-based eating aligns closely with the goals of environmental conservation.
Economic Benefits and Challenges
The growing interest in plant-based diets offers numerous economic benefits, both on individual and societal levels. For many individuals, transitioning to a plant-based diet can lead to significant cost savings. Plant-based staples like grains, legumes, and vegetables tend to be less expensive than meat and dairy products, providing an economical way to achieve a nutritious diet. Additionally, the reduction in healthcare costs associated with a decrease in diet-related diseases, such as cardiovascular issues and diabetes, further amplifies these financial benefits.
On a broader scale, the economic landscape undergoes substantial shifts due to the rising demand for plant-based products. Agricultural practices are adapting, with more land being dedicated to the cultivation of plant crops rather than livestock feed. This shift not only optimizes land use but also contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, as plant-based agriculture generally has a lower carbon footprint. Furthermore, the burgeoning plant-based industry has sparked entrepreneurial opportunities and created jobs, from farming and product development to marketing and retail, thereby stimulating economic growth.
Despite these benefits, several challenges complicate the widespread adoption of plant-based diets. The cost of certain plant-based meat and dairy alternatives can be prohibitively high for some consumers, potentially limiting accessibility. Innovations and economies of scale are needed to bring down these costs to make plant-based options more affordable for the general population.
Moreover, the transition toward plant-based diets poses significant economic implications for those entrenched in the traditional meat and dairy industries. Farmers and workers who rely heavily on livestock production may face economic instability as demand shifts. Mitigating these effects requires comprehensive support measures, such as retraining programs and subsidies, to help these communities adapt to the changing market conditions. Balancing the economic benefits and challenges is crucial for ushering in a more sustainable future while ensuring that all stakeholders can participate in and benefit from this dietary revolution.
Cultural Shifts and Acceptance
The rise of plant-based diets has marked a significant cultural shift, reflecting changing perceptions and an expanding acceptance across the globe. This dietary transformation is gaining traction in various cultures, driven by a combination of health consciousness, environmental concerns, and ethical considerations. One of the most compelling factors contributing to this shift is the influence of media and prominent figures. Influencers and celebrities advocating for plant-based diets have considerably impacted public opinion, making plant-based eating appear more accessible and desirable.
Traditional cuisines, which have been deeply rooted in meat and dairy-centric paradigms, are also evolving to accommodate plant-based options. For instance, many Asian cultures, historically reliant on tofu and legumes, are witnessing a resurgence in their traditional plant-based dishes. In the Mediterranean, with its rich legacy of plant-based ingredients like olives, grains, and vegetables, there is a renewed focus on incorporating these elements. Latin American diets are celebrating their ancestral grains, fruits, and vegetables, ensuring that plant-based eating remains both flavorful and authentic.
However, despite these positive trends, common misconceptions and barriers still exist. A notable misconception is that plant-based diets lack sufficient protein, which can be addressed through education on protein-rich plants such as lentils, chickpeas, and quinoa. Additionally, cultural and familial traditions can pose barriers to adopting plant-based diets. Strategies to overcome these obstacles include introducing plant-based dishes during festive meals or incorporating meat alternatives that mimic traditional flavors and textures, thus facilitating a smoother transition.
Ultimately, as cultures globally become more interconnected, the acceptance and integration of plant-based diets are likely to continue growing. By drawing from diverse culinary traditions and harnessing the power of influential voices, the movement towards plant-based eating can further embed itself within the varied tapestries of global cultures, aligning with both historical practices and contemporary values.
Tips for Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
Embarking on a plant-based diet can be an enriching journey toward a more sustainable lifestyle. Here are some practical tips to help you make a smooth transition:
Meal Planning: Begin by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes into your meals. Planning your week ahead can simplify this process and ensure you maintain a balanced diet. Start with a few plant-based meals a week and gradually increase the frequency as you become more comfortable.
Grocery Shopping: Familiarize yourself with the plant-based alternatives available at your local grocery store. Look for plant-based proteins such as tofu, tempeh, and legumes. Nowadays, many stores offer plant-based milk, cheese, and yogurt options, making it easier to find suitable substitutes for your favorite dairy products.
Plant-Based Substitutes: Find replacements for common animal products. For instance, opt for almond or soy milk instead of cow’s milk, or use nutritional yeast as an alternative to cheese in dishes. Be open to experimenting with different options until you find what works best for you.
Social Situations: Navigating social gatherings can be challenging. Communicate your dietary preferences beforehand and offer to bring a plant-based dish to share. This not only ensures you have something to eat but also introduces others to the appealing flavors of plant-based cuisine.
Balancing Nutrition: A well-rounded plant-based diet should include a variety of foods to meet all your nutritional needs. Incorporate a mix of proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains. Pay attention to key nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, which can be more challenging to obtain from plant sources.
Gradual Change: Transitioning to a plant-based diet is most sustainable when done gradually. Begin by making small changes, such as having one plant-based meal per day or trying a new vegan recipe each week. As you progress, you will find it easier to sustain these changes long-term.
Below is a sample meal plan to get you started:
Breakfast: Overnight oats with almond milk, chia seeds, and fresh berries.
Lunch: Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumber, tomato, and a lemon-tahini dressing.
Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables and brown rice.
Snack: Apple slices with almond butter.
Embrace this journey with enthusiasm and patience, and you’ll soon reap the benefits of a more sustainable and healthful lifestyle.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As we have explored throughout this discussion, the rise of plant-based diets marks a promising shift towards more sustainable living. The adoption of plant-based eating habits has numerous benefits for individual health, including the potential to reduce chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. This dietary change can also significantly lessen our environmental footprint by decreasing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water, and preserving biodiversity.
Moreover, the social and economic implications of a plant-based diet are profound. As consumer demand for plant-based options grows, the market responds with greater variety and innovation in food choices. This shift not only fosters a more inclusive food culture but also creates economic opportunities within the plant-based industry. From small-scale farmers specializing in organic produce to large corporations investing in plant-based product lines, the economic ripple effect is tangible and impactful.
Looking forward, individual and collective efforts will be instrumental in driving the momentum of this positive change. Consumer choices, advocacy for plant-based options in institutional settings, and supportive policies are all critical levers in mainstreaming plant-based diets. Additionally, educational campaigns and initiatives to raise awareness about the benefits of plant-based eating can significantly influence public perception and behavior.
Current trends indicate a continued rise in the popularity and acceptance of plant-based diets. Innovations in food technology, such as lab-grown meats and plant-based alternatives that closely mimic animal products, are likely to play a pivotal role in this evolution. As more people turn to plant-based diets, we can expect to see substantial benefits for public health, reduced environmental degradation, and a more sustainable approach to food production and consumption.
In conclusion, the transition to plant-based diets offers a path towards a healthier, more sustainable, and equitable future. By embracing plant-based eating patterns, we contribute to the well-being of our planet and ourselves. The collective impact of our choices can foster a resilient food system capable of nourishing the growing global population while preserving the natural resources that sustain life.








1 thought on “The Rise of Plant-Based Diets for a Sustainable Future”
Comments are closed.