Creativity in Problem-Solving
Creativity is often perceived as a distinct skill set primarily associated with the arts; however, it plays a critical role in problem-solving across various fields. At its core, creativity can be defined as the ability to generate original ideas, approaches, and solutions that are not only innovative but also functional. This fundamental ability enables individuals to step outside conventional boundaries, exploring new perspectives and methodologies while tackling complex challenges.
In today’s fast-paced, ever-evolving world, the significance of creativity in problem-solving cannot be overstated. Businesses, educators, healthcare professionals, and governments worldwide face multifaceted issues that require adaptable and inventive solutions. Here, creativity becomes a vital asset, empowering teams and individuals to identify unique paths and execute strategies that address the root causes of problems, rather than merely alleviating symptoms.
The interplay of creativity, problem-solving, and innovation is evident in various contexts. Creative problem solvers demonstrate not only the capacity to conceive original ideas but also the ability to apply them effectively to real-world situations. This connection highlights that true innovation stems from creative thinking, as it enables the radical shifts that propel industries forward and foster advancements in technology, policy, and social practices. Through harnessing creativity, individuals can transform challenges into opportunities, paving the way for sustained growth and improvement.
In essence, understanding creativity and its pivotal role in problem-solving equips individuals and organizations to navigate an increasingly complex landscape. Acknowledging this interdependence not only emphasizes the need for fostering creative environments but also underscores the importance of integrating creative thinking into standard problem-solving frameworks. Such an approach can lead to more effective and sustainable solutions in addressing contemporary issues.
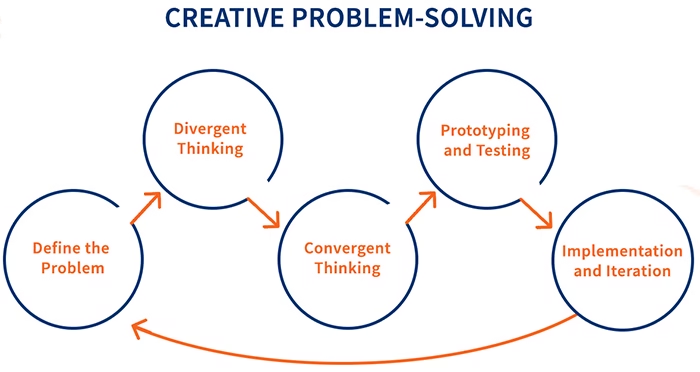
Understanding Problem-Solving: Traditional vs. Creative Approaches
Problem-solving is an essential skill that can determine the success of individuals and organizations alike. Traditional methods of problem-solving often emphasize established frameworks and logical reasoning, relying on step-by-step procedures drawn from previous experiences and analytical processes. These conventional approaches are generally linear and structured, benefiting from formulas and models that have been proven effective over time. However, while traditional problem-solving can be efficient, it may also lead to limitations, particularly in complex or novel situations that do not fit neatly into existing paradigms.
In contrast, creative problem-solving embraces a more flexible mindset. This approach encourages divergent thinking, which allows individuals to explore various possibilities and generate innovative ideas that may not arise from conventional methods. Creative problem-solving often involves brainstorming sessions, mind mapping, and other techniques designed to stimulate ideation. Such methods invite participants to think freely and explore unconventional solutions, ultimately expanding the range of potential outcomes and fostering a culture of innovation.
One significant limitation of traditional methods is their propensity to reinforce existing biases and norms. This can hinder the ability to identify underlying causes or to appreciate the broader context of a given problem. As a result, organizations may miss out on transformative opportunities that are only visible through the lens of creativity. Conversely, creative techniques can lead to breakthroughs by encouraging teams to question assumptions and challenge the status quo. This is vital in an ever-evolving world where adaptability and inventive thinking are paramount for addressing emerging challenges effectively.
Recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches is crucial for effective problem-solving. The integration of traditional and creative methodologies allows for a more holistic strategy, enabling problem-solvers to not only rectify existing issues but also innovate for the future. Through a balanced perspective, organizations can maneuver complex challenges while fostering an environment that champions creativity as a fundamental component of progress.

The Psychology of Creativity in Problem-Solving
Creativity plays a pivotal role in problem-solving and innovation, influencing how individuals approach challenges and devise solutions. Understanding the psychological aspects of creativity reveals critical cognitive processes that enhance creative thinking. Two prominent theories that define creative thought are divergent and convergent thinking. Divergent thinking emphasizes the generation of multiple possible solutions to a problem, fostering a broad exploration of ideas. In contrast, convergent thinking focuses on narrowing down those options to find the most effective solution. Both cognitive styles are essential for adept problem-solving and are often utilized in tandem.
Mental flexibility is a key characteristic that significantly enhances creative problem-solving abilities. Individuals with a high degree of mental flexibility can shift perspectives and adapt their thinking, enabling them to approach problems from various angles. This adaptability is crucial in navigating complex situations where traditional methods may fall short. Additionally, openness to experience, characterized by a willingness to entertain new ideas and experiences, is closely related to creativity. Those who are open-minded tend to explore a wider range of solutions, leading to more innovative outcomes.
Despite the inherent potential for creativity, several psychological barriers can inhibit this process. The fear of failure is a prevalent obstacle, often leading individuals to shy away from taking risks that could lead to innovative solutions. This apprehension may stem from a fixed mindset, where individuals believe their abilities are static rather than malleable. Cultivating a growth mindset, on the other hand, promotes resilience and encourages experimentation, ultimately fostering an environment where creative problem-solving can thrive.
In summary, the psychology of creativity in problem-solving encompasses a range of cognitive processes and theories. By understanding these elements, individuals can develop strategies to enhance their creative abilities, thereby improving their problem-solving capabilities and contributing to innovation.

Real-World Examples of Creative Problem-Solving
Creativity is a vital catalyst in the realm of problem-solving, serving as the driving force behind many significant innovations across various industries. A notable example can be drawn from the technology sector, particularly in the development of the smartphone. When Apple introduced the first iPhone in 2007, it disrupted the mobile phone market by providing a multifaceted device that integrated phone, internet browsing, and multimedia capabilities. The creative vision of combining these functions into one sleek piece of technology not only redefined communication but also gave rise to an entirely new industry around mobile applications.
Similarly, the healthcare industry has witnessed remarkable instances where creative problem-solving has led to improved patient outcomes. One poignant example is the development of the portable dialysis machine. Traditional dialysis treatments required patients to visit specialized centers multiple times a week, often leading to discomfort and inconvenience. Through innovative thinking and collaboration among engineers and medical professionals, a compact, portable device was designed, allowing patients to receive treatment in the comfort of their homes. This not only revolutionized the way patients manage their condition but also enhanced their quality of life.
The arts sector also showcases the transformative power of creativity in problem-solving. A striking example can be found in community art initiatives aimed at revitalizing urban spaces. In various cities, artists have collaborated with local governments to transform neglected areas through public murals and installations. These art projects not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of communities but also foster local pride and social cohesion, thereby addressing challenges like crime and urban decay. The creativity embedded in these initiatives exemplifies how innovative approaches can effect positive change in society.
Ultimately, these examples across technology, healthcare, and the arts underscore the significance of creative problem-solving. By harnessing the power of imagination and innovation, industries can overcome challenges and pave the way for transformative solutions that resonate on both individual and societal levels.

Fostering a Creative Mindset in Teams and Organizations
In today’s rapidly evolving work environment, fostering a creative mindset within teams and organizations becomes essential for driving innovation and addressing complex problems. Establishing a supportive atmosphere is crucial, where employees feel encouraged to experiment, collaborate, and remain open to new ideas. This approach not only advances problem-solving capabilities but also ensures that organizations thrive in a competitive landscape.
One effective method to encourage creativity is through brainstorming sessions. These collaborative meetings can generate a wealth of ideas, as diverse perspectives come together to tackle specific challenges or explore new opportunities. Implementing structured brainstorming techniques, such as round robin or brainwriting, can facilitate more inclusive participation, thereby increasing the volume and variety of generated concepts.
Mind mapping is another valuable technique that can stimulate creative thinking. By visually organizing thoughts, teams can uncover connections between ideas that may not be readily apparent. This approach not only promotes clarity in thought processes but also inspires innovative solutions by encouraging team members to explore their ideas more deeply. Mind mapping allows for a non-linear exploration of concepts, which is vital in a creative environment.
Additionally, embracing design thinking as a framework can enhance creativity within teams. This iterative methodology focuses on understanding user needs and defining problems, facilitating innovative solutions through prototyping and testing. By integrating design thinking practices, organizations can cultivate a culture that prioritizes empathy and experimentation, empowering employees to take risks in their problem-solving approaches.
Ultimately, fostering a creative mindset requires a commitment to establishing an environment that values collaboration, experimentation, and the exploration of new ideas. Organizations that implement these strategies are likely to see improved innovation, enhance employee satisfaction, and effectively tackle challenges in an ever-changing landscape.

Barriers to Creativity and How to Overcome Them
Creativity is essential for effective problem-solving and innovation; however, various barriers can hinder the creative process. Common obstacles include rigid organizational structures, limited time, and cultural resistance. These barriers can stifle new ideas and discourage individuals from exploring innovative solutions, ultimately impacting the overall effectiveness of teams and organizations.
Rigid organizational structures often create environments where creativity is not prioritized. Hierarchical systems can lead to a top-down approach in decision-making, which may discourage lower-level employees from sharing their ideas. To overcome this, organizations should consider redesigning their processes to encourage open communication and collaboration across all levels. This can be achieved through the establishment of cross-functional teams or innovation committees that gather diverse perspectives and facilitate brainstorming sessions.
Another significant barrier to creativity is the lack of time. In today’s fast-paced work environment, employees may feel pressured to prioritize immediate tasks over creative thinking. Organizations can address this challenge by allocating specific time for creativity workshops or brainstorming sessions. This not only allows employees to step away from their daily responsibilities but also fosters a culture that values innovative thinking as a key component of problem-solving.
Cultural resistance, including fear of failure or criticism, can also inhibit creativity. To counteract this, organizations should foster an inclusive culture that encourages diverse perspectives and supports risk-taking. Providing training programs can help employees develop a growth mindset, allowing them to view challenges as opportunities for learning rather than setbacks. Additionally, celebrating creative successes—no matter how small—can reinforce a positive attitude towards innovation.
By recognizing these barriers and implementing practical strategies, individuals and organizations can cultivate an environment conducive to creative problem-solving, ultimately leading to more innovative solutions.
The Link Between Creativity, Innovation, and Competitive Advantage
In today’s dynamic business environment, the interplay between creativity and innovation is paramount for sustaining a competitive advantage. Creativity, defined as the ability to generate novel ideas and concepts, serves as a catalyst for innovation. Innovation, which is the practical application of creative ideas, translates these concepts into products, services, or processes that meet emerging market needs. The symbiotic relationship between these two elements enables organizations to differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace.
The significance of creative problem-solving cannot be underestimated as it drives the development of unique offerings that capture consumers’ attention. Companies that foster a culture of creativity often lead the way in innovation. For instance, tech giant Apple exemplifies this linkage, having consistently introduced groundbreaking products that transform consumer expectations and experiences. Their focus on creativity in design and functionality has not only set them apart but has also established a loyal customer base, thus solidifying their market position.
Moreover, organizations like Google and Tesla demonstrate how innovation driven by creativity can result in a strong competitive edge. Google’s approach to creative collaboration and experimentation allows it to maintain a leadership position in search technology and advertising. Tesla, on the other hand, employs innovative engineering solutions and creative marketing strategies to redefine the automotive industry, promoting sustainable energy solutions while also appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
These real-world examples illustrate that organizations which embrace creativity and cultivate an environment conducive to innovative thinking are more likely to develop distinctive offerings. This proactive stance not only enhances their marketplace presence but also allows them to react swiftly to changing consumer demands, further cementing their competitive advantage. Ultimately, creativity is not merely an asset; it is a critical driver of innovation that shapes the future of businesses in an ever-evolving landscape.
Measuring Creativity and Its Impact on Problem-Solving
Assessing creativity, particularly in the context of problem-solving and innovation, is a multifaceted endeavor. Various metrics and frameworks have been developed to evaluate creative contributions. For instance, the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT) are widely used to assess individual creativity by measuring fluency, flexibility, originality, and elaboration in responses. Similarly, the Consensual Assessment Technique (CAT) allows evaluators to determine the creativity of work products by expert judgment, providing a qualitative approach to measurement.
Beyond individual assessment, measuring creativity within teams is crucial. Team creativity can significantly influence innovative solutions to complex problems. Frameworks such as the Four Cs of Creativity (mini-c, little-c, pro-c, and big-C) offer insight into different levels of creativity and help in aligning team efforts towards fostering innovative outcomes. In organizational settings, metrics that evaluate collaborative processes, such as the frequency of ideas generated and the diversity of input, play a vital role in understanding creative dynamics.
The impact of creativity on problem-solving outcomes is profound. Creative individuals and teams are better equipped to approach challenges from various angles, generating a rich diversity of solutions. This capability enhances critical thinking and adaptability, essential traits in today’s fast-paced environments. Moreover, methodical feedback and reflection are indispensable in cultivating creative capacities. Continuous feedback mechanisms encourage individuals and teams to refine their ideas and approaches, thus sustaining a cycle of innovation. Reflective practices enable individuals to learn from past experiences, integrating lessons that can lead to more effective problem-solving in the future.
Ultimately, the interplay between measuring creativity and its application to problem-solving is pivotal. By adopting robust evaluation methods and fostering a culture of feedback and reflection, organizations can enhance their creative capabilities, resulting in innovative solutions that address the complexities of modern challenges.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Throughout this discussion, we have explored the significant impact of creativity on problem-solving and innovation. Creativity acts as a catalyst, fostering fresh ideas and perspectives that lead to effective solutions in various contexts. By embracing a creative mindset, individuals and organizations alike can enhance their ability to tackle complex challenges and drive progress. The synergy between creativity and innovation is paramount; innovative solutions often stem from creative processes that challenge conventional thinking.
It is evident that nurturing creativity is not merely beneficial but essential in both personal and professional arenas. Encouraging an environment that supports imaginative thinking can ignite collaboration and motivate teams to explore diverse solutions. Creative strategies empower individuals to think outside the box, transforming obstacles into opportunities. Moreover, cultivating creativity can lead to a greater sense of fulfillment and engagement, both personally and within a team setting.
We encourage readers to actively participate in nurturing their creative skills. This can be achieved through various means, such as engaging in creative exercises, embracing new experiences, or collaborating with diverse teams. By doing so, one not only enhances their problem-solving capabilities but also contributes to a vibrant culture of innovation in their surroundings, whether it be in the workplace, educational institutions, or community initiatives.
In conclusion, the role of creativity in problem-solving and innovation is undeniable. By integrating creative approaches into everyday practices and supporting an innovative culture, we can collectively advance toward more effective solutions and a brighter future. We invite you to take the first step by adopting these practices and inspiring others to do the same, thus fostering a community where creativity thrives and innovation flourishes.