Introduction to TV Technologies
Which TV Technology is Right for You? The evolution of television technology has seen remarkable progress since the inception of the very first televisions in the early 20th century. Initially rooted in black-and-white displays, the introduction of color televisions marked a notable advancement, captivating audiences with enhanced visual experiences. This trajectory of innovation accelerated significantly over the past two decades, ushering in the development of advanced display technologies that cater to varying consumer needs and preferences. Among these, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode), QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode), and Mini-LED emerge as the frontrunners, each contributing uniquely to the landscape of modern televisions.
OLED technology, introduced to consumers in the late 2000s, revolutionized the way visuals are displayed. By allowing individual pixels to emit their own light, OLED screens achieve unparalleled contrast ratios and vibrant colors. This capability positions OLED as a favored choice for those seeking the richest color representation and deep blacks, ensuring cinematic experiences at home. In contrast, QLED technology, developed primarily by Samsung, leverages Quantum Dot technology to enhance color accuracy and brightness. While QLED TVs utilize a traditional LED backlight, the Quantum Dot layer significantly improves the color gamut, providing bright and vivid visuals, particularly in well-lit environments.
Furthermore, Mini-LED represents the latest advancement in LED display technology, utilizing smaller LEDs that enable more precise local dimming and improved contrast. This innovation facilitates greater control over lighting, ultimately enhancing picture quality and creating an immersive viewing experience. As these technologies continue to evolve, they each appeal to diverse market segments, from movie enthusiasts to casual viewers. Understanding the distinctions and strengths among OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED will enable consumers to make informed choices tailored to their specific viewing preferences in the current dynamic television market.

Understanding OLED Technology
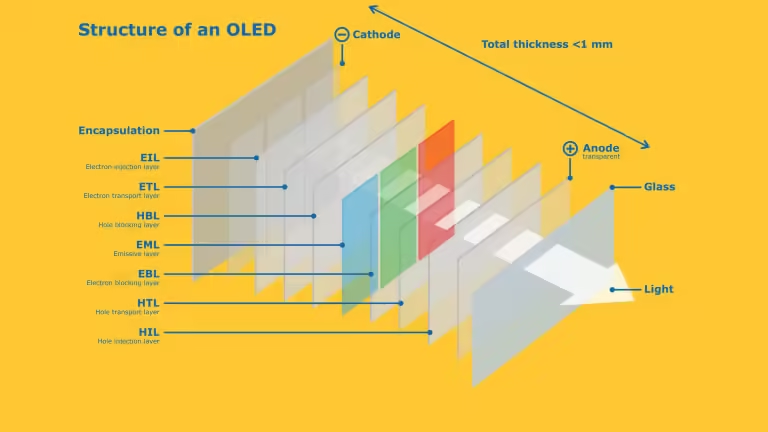
OLED, or Organic Light Emitting Diode, is a television technology that stands out in the market due to its unique method of producing images. Unlike traditional LCDs that rely on a backlight, OLED displays utilize organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through them. This feature enables each pixel to emit its own light, allowing for the true self-lighting properties of OLED technology. Consequently, OLED TVs can achieve individual pixel brightness levels, which fosters the ability to display exceptionally deep blacks and a remarkable contrast ratio.
One of the most significant advantages of OLED technology is its color accuracy. Since the pixels emit light independently, they can create a vast spectrum of colors, resulting in vibrant and lifelike images. The thin profile of OLED panels also allows for sleek designs, making them aesthetically appealing in any living space. This combination of high color fidelity and an ultra-slim design positions OLED as a leading choice for home theater enthusiasts who seek the best visual experience.
However, OLED technology is not without its drawbacks. A common concern among users is the potential for burn-in, where static images can leave a permanent mark on the screen if displayed for extended periods. This issue arises because organic materials degrade over time, particularly when exposed to consistent, high-contrast visuals. Additionally, the cost of OLED TVs tends to be higher than that of their competitors, such as QLED and Mini-LED displays, which might be a consideration for budget-conscious consumers.
Exploring QLED Technology
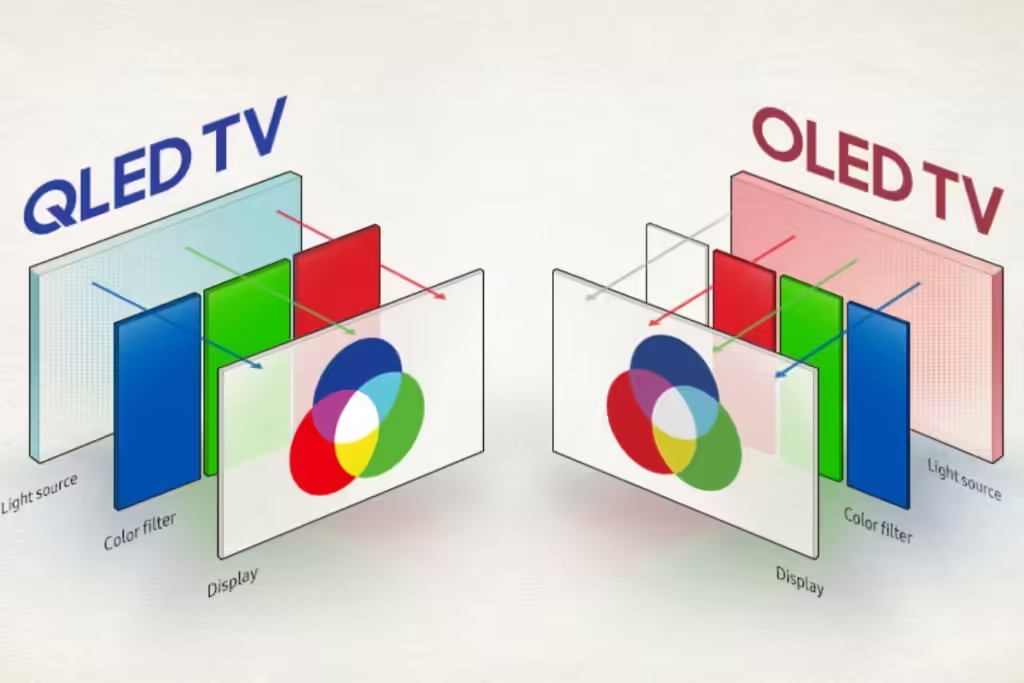
Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED) technology has become increasingly popular in the realm of television displays, particularly due to its distinctive approach to producing vibrant images. At its core, QLED employs quantum dots, which are microscopic semiconductor particles that emit specific colors when exposed to light. These quantum dots are positioned in front of an LED backlight, creating a stunning visual display that enhances color accuracy and vividness.
One of the primary advantages of QLED technology is its impressive brightness levels. QLED televisions can achieve significantly higher brightness than many OLED displays, making them particularly suitable for well-lit environments. This feature is particularly advantageous for viewers who enjoy watching television during the day or in brightly lit rooms, as it ensures that images remain dynamic and engaging. Furthermore, the color gamut offered by QLED is often expansive, providing a wider array of colors that can be displayed with incredible accuracy.
Despite its many benefits, QLED technology does face certain challenges. One notable drawback is its limited viewing angles. While direct viewers may experience exceptional image quality, those watching from an angle may notice distortion in color and contrast, something that OLED displays generally excel at handling. Additionally, the contrast ratio of QLED screens, which is primarily determined by the quality of the backlighting, is generally lower than that of OLED televisions. This difference means that dark scenes may not appear as deep or immersive on QLED screens compared to their OLED counterparts.
In conclusion, QLED technology offers remarkable brightness and vibrant colors, making it a strong contender for those seeking high-quality television displays. However, potential purchasers should weigh these benefits against the viewing angle and contrast limitations when deciding on the most suitable TV technology for their needs.

Introduction to Mini-LED Technology
Mini-LED technology represents a significant advancement in the realm of display technology, offering a novel approach to backlighting that enhances picture quality and performance. This innovation utilizes smaller LEDs than traditional backlighting methods, allowing for more precise control over brightness and contrast. Mini-LEDs can be packed densely behind an LCD panel, increasing the number of local dimming zones. This results in greater contrast ratios, producing deeper blacks and more vibrant colors, even in scenes that feature extreme brightness and darkness simultaneously.
One of the primary benefits of Mini-LED technology is its ability to deliver improved brightness control. With a higher number of independently controlled zones, Mini-LED TVs can achieve impressive peak brightness levels without the blooming effect commonly associated with standard LED-backlit televisions. This feature is particularly advantageous in high dynamic range (HDR) content, as it enables a more realistic and immersive viewing experience. The increased efficiency of Mini-LED backlighting also contributes to enhanced energy savings, making this technology appealing not only for its performance but also for its potential sustainability benefits.
As an emerging technology, Mini-LED sits firmly between OLED and QLED in the market spectrum. While QLED utilizes quantum dot technology for enhanced color and brightness, and OLED boasts impeccable contrast due to its self-emissive nature, Mini-LED combines the strengths of both without some of their respective limitations. For instance, unlike OLED, Mini-LED does not suffer from burn-in, making it a more resilient option for varied content consumption. Furthermore, compared to QLED, Mini-LED offers superior black levels due to its more refined control of backlighting. This evolving technology holds promise for those seeking high-quality viewing experiences, representing a compelling choice for consumers weighing the merits of OLED versus QLED technologies.
Comparing Key Features of OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED
When comparing OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED, several key factors come into play: black levels, brightness, color accuracy, viewing angles, and lifespan. Here’s how each technology performs in these areas.
Black Levels and Contrast
- OLED: OLED excels in black levels and contrast. Each pixel in an OLED display can turn off completely, creating true blacks and an infinite contrast ratio. This feature is crucial for viewing dark scenes in movies or shows, as it prevents the grayish look seen on other display types.
- QLED: QLED TVs, while bright and vivid, cannot achieve the same true black levels as OLED. The LED backlight is always on to some degree, which can lead to light bleeding into dark areas, reducing contrast. Some high-end QLED TVs use local dimming to improve contrast but are still no match for OLED.
- Mini-LED: Mini-LED offers a middle ground. With more dimming zones than traditional LED-LCD TVs, Mini-LED can achieve deeper blacks than QLED but still doesn’t match the precision of OLED. High-end Mini-LED models come close to OLED’s black levels in certain conditions.
Brightness
- OLED: OLED panels can be bright enough for most viewing environments, but they don’t reach the brightness levels of QLED or Mini-LED. OLED’s peak brightness can be limited, especially when displaying large bright areas, making them less ideal for rooms with a lot of ambient light.
- QLED: QLED technology, particularly in premium models, excels in brightness, often reaching 1,500-2,000 nits or more. This makes QLED the preferred choice for well-lit rooms or outdoor use.
- Mini-LED: Mini-LED TVs also achieve high brightness, often comparable to QLED. The increased number of LEDs in the backlight helps to reach high peak brightness levels without compromising color accuracy.
Color Accuracy and Volume
- OLED: OLED displays offer excellent color accuracy and wide color gamut coverage, particularly in darker scenes. However, at very high brightness, colors can appear slightly less vibrant than on QLED.
- QLED: QLED, with quantum dot technology, excels in color accuracy and brightness. This is especially evident in bright scenes, where colors stay vivid and accurate even at high brightness levels.
- Mini-LED: Mini-LED can also deliver impressive color accuracy, especially on models that include quantum dots. High-end Mini-LED TVs with quantum dots provide colors similar to QLED, making them competitive in terms of color performance.
Viewing Angles
- OLED: OLED offers the best viewing angles among these technologies. Because each pixel emits light directly, OLED screens maintain color and contrast even at sharp angles.
- QLED: QLED TVs typically struggle with viewing angles, with colors and contrast diminishing when viewed from the side. Some high-end QLED models attempt to mitigate this with improved panel designs.
- Mini-LED: Mini-LED has similar issues to QLED regarding viewing angles, although some premium models offer improvements that reduce color shift at wider angles.
Lifespan and Burn-In
- OLED: OLED screens are susceptible to burn-in, which can occur if static images are left on the screen for extended periods. However, modern OLEDs have various technologies to mitigate this risk, and burn-in is less of an issue for most users.
- QLED: QLED technology is not prone to burn-in, making it a good choice for users who plan to use the TV for extended gaming sessions or channels with static logos.
- Mini-LED: Like QLED, Mini-LED TVs don’t suffer from burn-in, making them suitable for varied content viewing without the risk of permanent image retention.
Gaming Performance Assessment
When it comes to gaming performance, the choice of television technology—OLED, QLED, or Mini-LED—can significantly influence the overall experience. Key metrics, such as response times, refresh rates, and HDR support, play crucial roles in optimizing gaming scenarios. Each technology offers distinct advantages and drawbacks, making it essential to understand their performance capabilities.
OLED technology is renowned for its rapid response times, usually clocking in at 1ms or less. This swift response ensures minimal motion blur during high-action gaming, which can be particularly beneficial in fast-paced genres such as first-person shooters. Furthermore, OLED displays offer stunning contrast ratios and rich colors, providing immersive visuals that enhance the gaming experience. However, one potential concern for gamers is the risk of image retention, also known as burn-in, especially if static images are displayed for prolonged periods.
In contrast, QLED TVs, powered by quantum dot technology, generally have slightly slower response times, averaging around 5-10ms. However, they excel in brightness and color accuracy, making them suitable for well-lit environments. QLED displays also support high refresh rates, often exceeding 120Hz, which is particularly advantageous for competitive gaming. Moreover, with the latest advancements in HDR support, QLED TVs can deliver vibrant and detailed images, further enhancing gameplay.
Mini-LED technology sits between OLED and QLED in terms of performance metrics. It uses a large array of small LEDs for backlighting, allowing for better control over local dimming, which results in improved contrast management. Mini-LED TVs usually achieve refresh rates of up to 120Hz and provide commendable response times, though they may not quite match the speed and precision of OLED. Additionally, their HDR capabilities rival those of QLED, providing a balanced gaming performance suited for various titles.
In summary, while OLED stands out for its response times and contrast, QLED and Mini-LED offer competitive refresh rates and brightness levels. The best choice ultimately depends on the specific gaming preferences and environments of the user, making it crucial to evaluate each technology’s strengths and weaknesses before making a decision.
Pros and Cons of Each Technology
OLED
Pros:
- Perfect black levels and infinite contrast
- Wide viewing angles
- Excellent color accuracy in dark scenes
Cons:
- Limited peak brightness compared to QLED and Mini-LED
- Susceptible to burn-in with prolonged static images
- Higher cost, especially for larger screen sizes
QLED
Pros:
- Exceptional brightness, ideal for bright rooms
- Great color accuracy and saturation in bright scenes
- Resistant to burn-in
Cons:
- Limited viewing angles on many models
- Black levels are not as deep as OLED
- Higher-end models can be expensive
Mini-LED
Pros:
- High brightness, close to QLED
- Improved black levels and contrast over traditional LED-LCD
- No risk of burn-in
Cons:
- Black levels and contrast aren’t as perfect as OLED
- Viewing angles can be limited
- More costly than standard LED-LCD TVs

Best Use Cases for OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED
OLED
OLED TVs are ideal for:
- Cinematic Viewing: If you enjoy watching movies or shows in a dark room, OLED’s deep blacks and rich contrast create a theater-like experience.
- Color and Detail Enthusiasts: The nuanced color and detail in darker scenes make OLED the choice for purists who value picture quality.
- Gaming: Many OLEDs support HDMI 2.1 features, like variable refresh rate and low input lag, making them excellent for gamers.
QLED
QLED TVs are ideal for:
- Bright Room Viewing: If your TV is in a well-lit room, QLED’s brightness ensures the picture stays clear and vivid.
- Sports and Events: For fast-moving content, like sports, QLED’s high brightness and color saturation provide a dynamic viewing experience.
- Long-Term Use: If you’re concerned about burn-in from static images, QLED’s durability is advantageous.
Mini-LED
Mini-LED TVs are ideal for:
- Balanced Performance: Mini-LED offers a middle ground, with good brightness and improved black levels, making it versatile for different room conditions.
- Cost-Conscious Shoppers: Mini-LED is often more affordable than OLED, offering strong performance at a more accessible price.
- Mixed Usage: Ideal for households that watch a mix of content in various lighting conditions.

Viewing Environment Considerations
When selecting a television technology, understanding how the viewing environment interacts with the characteristics of OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED TVs is crucial. Each technology presents distinct advantages and limitations depending on the room’s lighting conditions, seating distance, and reflective surfaces.
OLED TVs, known for their ability to display perfect blacks and vibrant colors, perform optimally in darker environments. Their self-illuminating pixels allow them to achieve excellent contrast ratios, making them ideal for home theaters or rooms with controlled lighting. However, in brightly lit areas, the general loss of brightness can diminish the viewing experience, especially in scenes with high dynamic range.
In contrast, QLED TVs, which utilize quantum dot technology to enhance brightness and color accuracy, shine in brighter rooms. They can effectively combat ambient light, making them suitable for living spaces with large windows or artificial lighting. The higher brightness levels help to mitigate color washout, allowing images to remain vivid under various lighting conditions. However, their reliance on backlighting can lead to reduced contrast in darker scenes compared to OLED displays.
Mini-LED technology serves as a middle ground, leveraging smaller LEDs for backlighting to improve contrast and brightness management. This technology can be advantageous in mixed-lighting environments, delivering enhanced detail in shadows and highlights. When determining the seating distance, it is essential to consider the resolution of the display as well — larger screens become more immersive when viewed from a greater distance, and a higher resolution will ensure clarity at that distance.
Ultimately, choosing the right technology—OLED, QLED, or Mini-LED—should involve an assessment of your specific viewing conditions, including how much natural light enters the room, the layout of your seating arrangement, and the type of entertainment consumed. Making an informed decision will lead to a more satisfying viewing experience tailored to your unique environment.
Cost and Availability
When it comes to selecting a television technology, cost and availability are critical factors that often influence purchasing decisions. OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED televisions each come with their respective price ranges, reflecting differences in technology, display performance, and brand positioning.
OLED televisions are known for their exceptional picture quality, characterized by deep blacks and vibrant colors. However, this superior performance typically comes at a higher price point, with OLED models generally ranging from mid to high-end pricing tiers. Consumers can expect entry-level 55-inch OLED TVs to start around $1,200, while larger or premium models can surpass $3,000. Additionally, the availability of OLED TVs, while steadily improving, may still be somewhat limited in certain markets compared to other technologies.
On the other hand, QLED televisions, which utilize quantum dot technology to enhance color accuracy and brightness, are often more affordable. Prices for QLED TVs vary significantly, starting around $800 for basic models and extending up to $3,500 for advanced versions, especially those boasting larger screen sizes and higher resolutions. As Samsung dominates the QLED market, consumers may find a broader selection and availability, making it easier to compare options and prices.
Lastly, Mini-LED technology, which combines elements of both OLED and traditional LED displays, is emerging as a promising alternative. Mini-LED TVs currently sit in a mid-range price category, starting at approximately $1,000 and reaching up to $3,000 for high-end models. While the availability of Mini-LED TVs is increasing, consumers should keep an eye on the rapidly evolving market, as new models are frequently introduced.
When considering warranty factors, it is essential to evaluate the long-term costs associated with each technology. A comprehensive warranty can mitigate potential repair expenses associated with high-end televisions. Therefore, consumers should factor in both the initial investment and the potential for future costs when deciding on the best television technology for their needs.

Conclusion: Which TV is Right for You?
Choosing the right television technology requires careful consideration of one’s viewing habits, preferences, and budget. Each technology—OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED—offers unique strengths and weaknesses that cater to specific needs. For instance, OLED displays are well-regarded for their exceptional color accuracy and infinite contrast ratios, making them ideal for movie enthusiasts who value immersive cinematic experiences. The deep blacks and vibrant colors of OLED screens enhance dark scenes, providing a level of detail that captivates viewers.
On the other hand, QLED technology shines in bright environments. With the ability to produce high levels of brightness and vibrant colors, QLED TVs are particularly suitable for viewers who watch in well-lit rooms. Gamers, in particular, may find QLEDs appealing due to their excellent motion handling and lower input lag, which can enhance the gaming experience. Additionally, QLEDs are generally known for their longevity and resistance to screen burn-in, further appealing to those who utilize their TV for various purposes.
Mini-LED technology, an innovative advancement, combines benefits from both OLED and QLED. This technology excels in providing improved black levels and enhanced contrast, thanks to its ability to control local dimming zones more effectively than traditional LED displays. Prospective buyers interested in future-proofing their purchase should consider Mini-LED, as it offers a balance of excellent performance across diverse viewing scenarios.
Ultimately, the choice between OLED, QLED, and Mini-LED boils down to personal preference and the viewer’s unique requirements. Casual watchers may appreciate the versatility of Mini-LED, while those seeking the utmost visual fidelity might lean toward OLED. Gamers and bright-room viewers could gravitate toward QLED. Therefore, understanding each technology’s distinctions will empower viewers to make informed decisions, ensuring they select the best-TV technology tailored to their lifestyle.