The global fish processing market has seen significant transformation in recent years, largely due to the rapid growth of the frozen fish sector. As one of the fastest-growing categories in the seafood industry, frozen fish is revolutionizing how fish is processed, stored, and consumed worldwide. Several factors, including technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and an increasing emphasis on sustainability, have fueled this “Frozen Fish Revolution.”
In this detailed exploration, we’ll cover the trends and insights driving this transformation, from market dynamics and consumer preferences to technological breakthroughs and regional market nuances. We will also explore the challenges and future outlook for the global frozen fish market.
Introduction to the Frozen Fish Market
Frozen fish has become a critical component of the global seafood market, offering convenience, longer shelf life, and greater accessibility to consumers around the world. Historically, frozen seafood was seen as inferior to fresh fish due to perceptions of poor quality and flavor. However, innovations in freezing technology, combined with modern supply chains, have dramatically improved the quality of frozen fish, making it comparable to, and in some cases superior to, fresh fish in terms of taste and nutrition.

The global demand for seafood is increasing due to rising population growth, increased awareness of the health benefits of fish, and changing dietary preferences. This surge in demand is pushing the fish processing industry to adopt new methods that meet both consumer needs and environmental sustainability standards.
As part of this revolution, frozen fish now accounts for a large portion of the global seafood supply, with market forecasts predicting continued growth in the coming years.
1. Market Overview: The Growth of Frozen Fish
1.1 The Global Demand for Fish and Seafood
Seafood has long been a dietary staple in many cultures, and the global demand for fish and seafood continues to grow. Fish is recognized as an excellent source of high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, all of which contribute to improved heart and brain health. As consumers become increasingly health-conscious, they are turning to seafood as a more nutritious alternative to red meat and other protein sources.
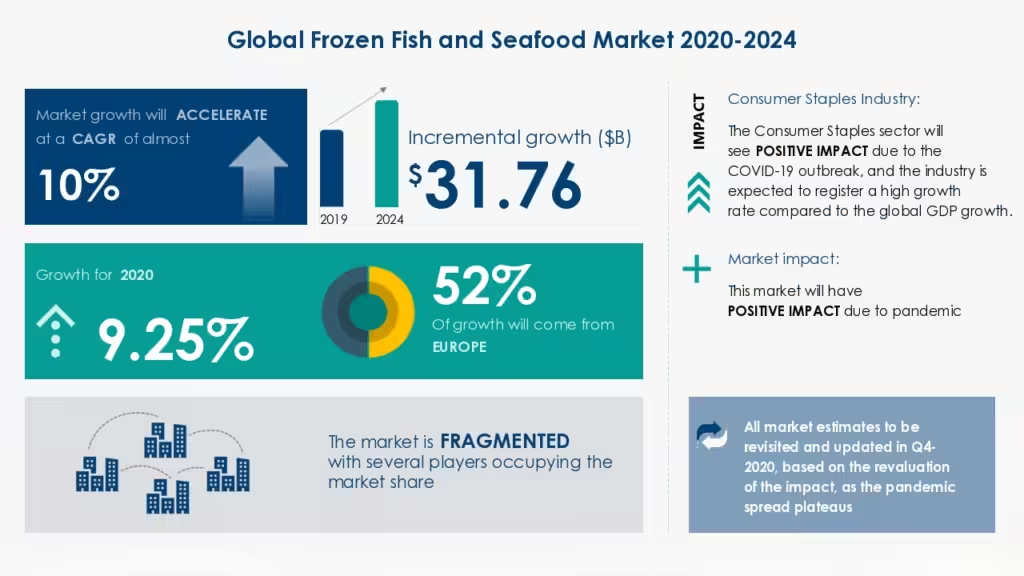
This rise in seafood consumption is accompanied by an increase in the demand for frozen fish. In 2022, the global fish processing market was valued at around USD 220 billion, with frozen fish accounting for nearly 60% of the total market share. Experts predict that this figure will rise as frozen fish products gain further traction, especially in emerging markets where fresh fish supply chains are more challenging to manage.
1.2 The Convenience of Frozen Fish
Frozen fish’s convenience factor is one of the primary reasons for its growing popularity. For today’s busy consumers, frozen fish offers the ability to store seafood for extended periods without compromising on quality. This makes it easier for individuals and families to incorporate fish into their daily meals without having to rely on frequent trips to grocery stores or fish markets.
Furthermore, frozen fish comes in various ready-to-cook formats, including fillets, fish sticks, and pre-seasoned products, which appeal to consumers who value convenience and ease of preparation. This is especially relevant in urbanized areas, where time constraints and busy lifestyles drive demand for convenient food options.
1.3 The Role of Urbanization and Lifestyle Changes
Urbanization has significantly contributed to the rise of frozen fish consumption. As populations migrate to cities, access to fresh fish becomes more difficult, while frozen fish offers a viable alternative. Urban consumers often face logistical challenges in procuring fresh fish, particularly in regions where coastal access is limited, or infrastructure for fresh seafood supply chains is underdeveloped. Frozen fish bridges this gap, providing a solution that is both convenient and cost-effective.
Moreover, changing lifestyles, including the shift toward dual-income households, has led to an increased reliance on frozen and processed foods. Consumers value products that offer quick preparation times without sacrificing nutritional value. As a result, frozen fish products have seen widespread adoption across various consumer segments, including working professionals, families, and health-conscious individuals.
2. Technological Advancements in Freezing Methods
2.1 The Evolution of Freezing Technology
Freezing technology has evolved significantly, revolutionizing the way fish is processed and stored. Modern freezing techniques preserve fish at its peak freshness, maintaining its taste, texture, and nutritional value. These advancements have helped overcome the stigma that frozen fish is inferior to fresh fish, leading to greater consumer acceptance.
The two most prominent freezing methods used in the fish processing industry are flash freezing and cryogenic freezing. These methods have not only improved the quality of frozen fish but also extended its shelf life, making it a more viable option for consumers and retailers alike.

2.2 Flash Freezing: The Key to Freshness
Flash freezing, also known as “quick freezing,” is one of the most widely used freezing techniques in the fish processing industry. The process involves freezing fish at extremely low temperatures (-18°C or lower) within a short period of time, typically within minutes of being caught. This rapid freezing process prevents the formation of large ice crystals, which can damage the fish’s cellular structure and degrade its texture and flavor.
Flash freezing is highly effective in preserving the freshness of fish, ensuring that it retains its natural taste, color, and nutritional content. The fish is frozen at its peak freshness, which makes it comparable to, and sometimes even better than, fresh fish that has been stored for several days.
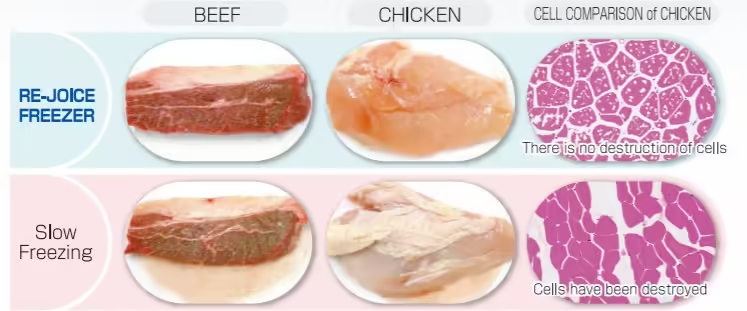
Many consumers are now familiar with the term “flash frozen,” and it has become a selling point for frozen seafood products. Retailers and restaurants highlight this technique as a way to assure customers of the quality and freshness of the product.
2.3 Cryogenic Freezing: Cutting-Edge Technology
Cryogenic freezing is an advanced method that uses liquid nitrogen to freeze fish in seconds. This process is typically used for premium fish products and ensures that the fish’s natural texture and taste are preserved. Cryogenic freezing is particularly effective for delicate species like shrimp and scallops, which can suffer from texture degradation during traditional freezing methods.
While cryogenic freezing is more expensive than other freezing techniques, it is growing in popularity due to its ability to maintain the quality of high-value fish products. This method is commonly used by high-end seafood producers and specialty retailers who cater to discerning customers seeking premium, restaurant-quality seafood.

2.4 Innovations in Packaging and Storage
The success of frozen fish products is not solely dependent on freezing technology; packaging also plays a crucial role. Modern packaging innovations, such as vacuum-sealed packaging and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), help preserve the freshness of frozen fish by minimizing exposure to oxygen and preventing freezer burn.
Vacuum-sealed packaging, for example, removes air from the packaging before sealing, which helps extend the shelf life of frozen fish and prevents ice crystals from forming. MAP, on the other hand, replaces the air inside the packaging with a gas mixture that slows down the oxidation process, further enhancing the longevity and quality of frozen fish products.
These packaging innovations have made frozen fish more appealing to consumers by ensuring that the product maintains its quality from the moment it leaves the processing plant until it reaches the consumer’s kitchen.

3. Sustainability and the Frozen Fish Market
3.1 Addressing Overfishing and Environmental Concerns
The global fish processing industry faces growing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, particularly in response to concerns about overfishing, habitat destruction, and the depletion of marine ecosystems. Overfishing threatens the long-term viability of fish populations, and it has become increasingly important for the industry to adopt measures that ensure the sustainability of fish stocks.
Frozen fish can play a significant role in promoting sustainability within the seafood industry. By extending the shelf life of fish, frozen products reduce the need for frequent fishing, which can help alleviate pressure on fish populations. Additionally, the frozen fish supply chain allows for more efficient use of resources, reducing waste and minimizing the environmental impact of seafood production.

3.2 Reducing Food Waste
One of the key sustainability benefits of frozen fish is its ability to reduce food waste. Fresh fish has a relatively short shelf life, and if not consumed within a few days, it often goes to waste. In contrast, frozen fish can be stored for months or even years without spoiling, providing consumers with greater flexibility in terms of meal planning and reducing the likelihood of food waste.
Food waste is a major environmental issue, as it contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and depletes natural resources. By opting for frozen fish, consumers can play a role in reducing food waste, which in turn supports global efforts to combat climate change and promote more sustainable food systems.
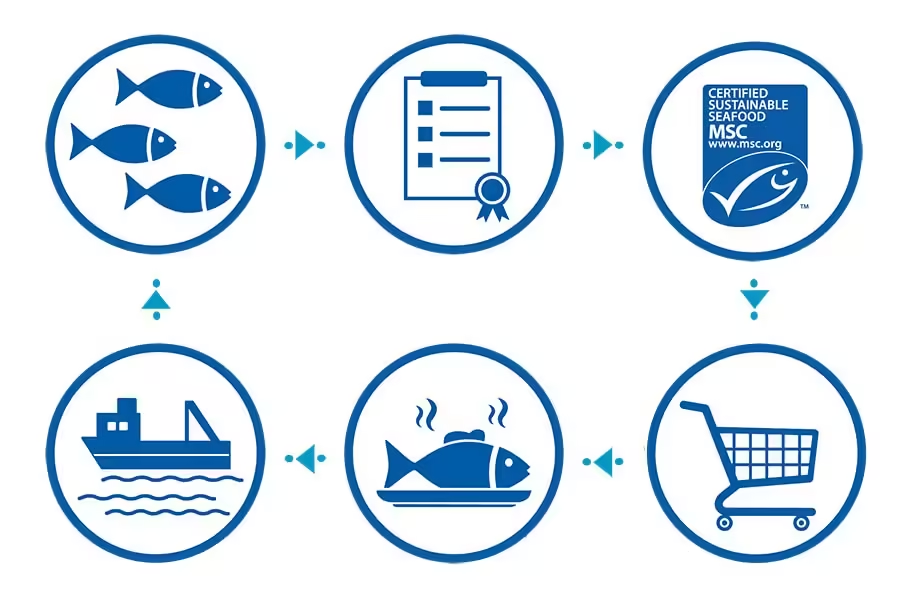
3.3 Sustainable Fishing Practices and Certifications
As sustainability becomes a top priority for consumers and businesses alike, the frozen fish market is increasingly focusing on responsible sourcing practices. Many companies are now partnering with certified fisheries to ensure that their products are sourced from well-managed fish stocks that adhere to strict environmental standards.
The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) certification is one of the most recognized eco-labels for sustainable seafood. It ensures that fish is sourced from fisheries that are committed to maintaining healthy fish populations, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting local communities. Frozen fish products that carry the MSC certification provide consumers with the assurance that their purchase supports sustainable fishing practices.
In addition to MSC certification, other labels, such as the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) and Global G.A.P., certify farmed seafood products, ensuring that they meet sustainability and ethical standards. These certifications have become increasingly important in the frozen fish market, as consumers seek out products that align with their values and contribute to the preservation of marine ecosystems.

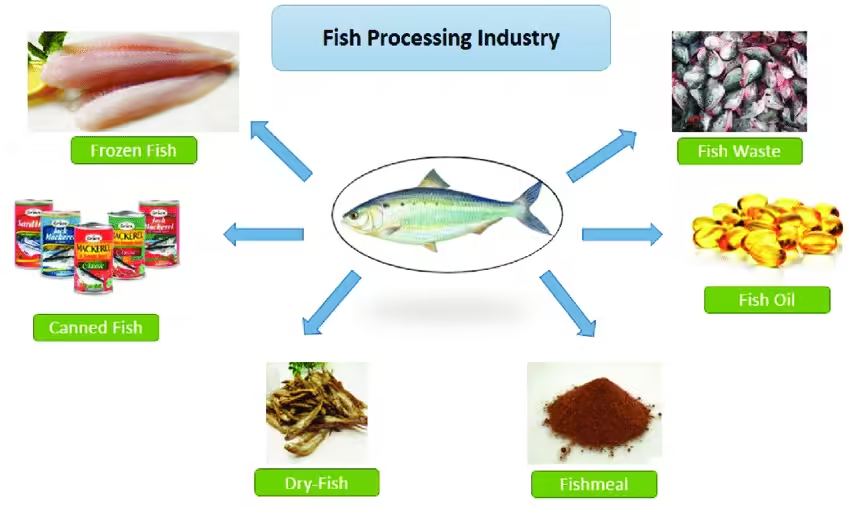
4. Market Segmentation: Categories and Species
4.1 Frozen Fish by Category: A Breakdown
The frozen fish market can be broadly segmented into three main categories: whole frozen fish, frozen fillets, and processed frozen seafood products. Each of these categories caters to different consumer needs and preferences, and they collectively drive the growth of the global frozen fish market.
- Whole Frozen Fish: This category includes fish that is frozen in its entirety, either gutted or with minimal processing. Whole frozen fish is popular among consumers who prefer to prepare fish from scratch or in traditional recipes. This category is particularly popular in regions where whole fish is commonly consumed, such as in parts of Asia and Africa.
- Frozen Fillets: Frozen fillets are pre-cut portions of fish that have been processed and deboned. This category is popular in Western markets, where consumers prefer the convenience of ready-to-cook products. Fillets are available in various types of fish, including salmon, cod, tilapia, and haddock.
- Processed Frozen Seafood Products: This category includes value-added products such as fish sticks, breaded fillets, and seafood patties. These products are highly popular in the fast-food and convenience food sectors, offering consumers a quick and easy way to prepare seafood dishes.
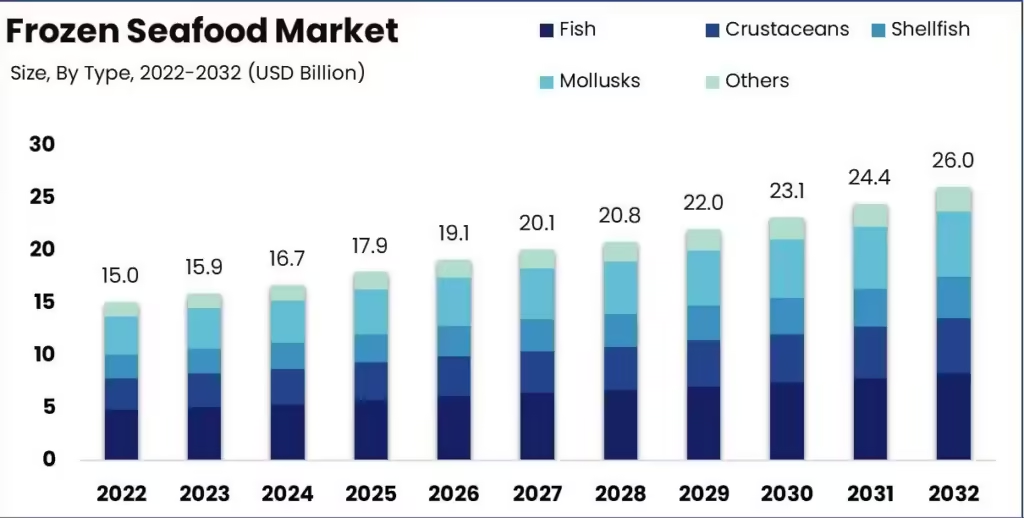
4.2 Species-Specific Insights: Fish, Crustaceans, and Mollusks
The frozen fish market encompasses a wide variety of species, each with its own market dynamics and consumer demand. The most popular species in the frozen fish market include whitefish (such as cod, haddock, and pollock), salmon, tuna, shrimp, and mollusks like squid and octopus.
- Whitefish: Whitefish, such as cod and haddock, are staples in the frozen fish market. These species are widely available in fillet form and are commonly used in processed products like fish sticks and breaded fillets. Whitefish is highly versatile and appeals to a broad range of consumers.
- Salmon: Salmon is one of the most popular fish species in the global frozen market due to its rich flavor, high nutritional value, and versatility in cooking. Frozen salmon fillets are widely available, and the species is a favorite among health-conscious consumers for its omega-3 content.
- Tuna: Tuna is another highly sought-after species in the frozen fish market, particularly for use in sushi, sashimi, and canned products. Frozen tuna is often processed into steaks or loins and is widely used in both home cooking and the restaurant industry.
- Crustaceans and Mollusks: Frozen shrimp, crab, squid, and octopus are also important segments of the frozen seafood market. Crustaceans like shrimp are particularly popular in the United States, Europe, and Asia, where they are used in a variety of dishes, from appetizers to main courses.
5. Regional Insights: Key Markets and Emerging Trends
5.1 North America and Europe: Leading Markets for Frozen Fish
North America and Europe are two of the largest markets for frozen fish, driven by increasing demand for convenience foods and health-conscious diets. In these regions, frozen fish is widely available in supermarkets and grocery stores, and consumers have access to a broad range of species and product formats.
In the United States, frozen fish products have gained popularity in recent years due to growing awareness of the health benefits of seafood. The demand for frozen fish is further bolstered by the rise of online grocery shopping and meal delivery services, which offer consumers easy access to frozen seafood products.
Similarly, Europe has seen significant growth in the frozen fish market, particularly in countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, and France. European consumers value the convenience of frozen fish and appreciate the long shelf life that allows them to stock up on seafood without worrying about spoilage.
5.2 Asia-Pacific: A Growing Market for Frozen Fish
The Asia-Pacific region is both a major producer and consumer of frozen fish. Countries like China, Japan, and India are key players in the frozen fish market, with strong demand for both domestic consumption and export. In particular, China and Vietnam are leading exporters of frozen seafood products, supplying fish to markets around the world.
In Japan, frozen fish is widely used in both traditional and modern cuisine, with species like tuna, salmon, and squid being especially popular. The country’s well-developed cold chain infrastructure supports the widespread distribution of frozen fish, ensuring that high-quality seafood is available to consumers across the country.
India is also seeing rapid growth in the frozen fish market, driven by rising income levels and increasing urbanization. Frozen fish is becoming more accessible to consumers in urban areas, where fresh fish is often harder to find. The Indian government’s focus on developing cold storage infrastructure is expected to further boost the growth of the frozen fish market in the coming years.
5.3 Emerging Markets: Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East
Emerging markets in Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East are also experiencing growth in the frozen fish market. In these regions, the development of cold storage facilities and improvements in transportation infrastructure have made frozen fish more accessible to consumers.
In Latin America, countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are seeing rising demand for frozen fish, particularly as consumers become more aware of the health benefits of seafood. In Africa, frozen fish is becoming a key component of food security, providing a stable source of protein in regions where access to fresh fish is limited.
The Middle East is another growing market for frozen fish, with increasing demand for species like shrimp, squid, and tilapia. The region’s reliance on imported seafood has made frozen fish a popular choice for consumers and businesses alike.
6. Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
6.1 Health and Wellness: A Key Driver of Frozen Fish Consumption
The global health and wellness trend has been a major driver of growth in the frozen fish market. As consumers become more health-conscious, they are seeking out nutrient-dense foods that support their overall well-being. Fish is widely regarded as a “superfood” due to its high content of omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and essential vitamins and minerals.
Frozen fish offers consumers a convenient way to incorporate seafood into their diets without compromising on nutritional value. Unlike some processed foods, frozen fish retains most of its nutrients, making it an ideal choice for health-conscious individuals who want to enjoy the benefits of fish without the hassle of cooking from scratch.
Additionally, frozen fish is seen as a safer option compared to fresh fish, as freezing kills harmful bacteria and parasites that may be present in raw seafood. This is particularly important for consumers who are concerned about food safety and want to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.

6.2 The Rise of Convenience Foods
The demand for convenience foods has skyrocketed in recent years, particularly among urban consumers who lead busy lifestyles. Frozen fish products, such as pre-packaged fillets, fish sticks, and seafood meals, cater to this growing demand for quick and easy meal solutions.
Frozen fish offers the advantage of being ready-to-cook, allowing consumers to prepare healthy and delicious meals with minimal effort. This has made frozen fish products popular among working professionals, families, and individuals who value convenience without compromising on nutrition.
The rise of e-commerce and online grocery shopping has further boosted the popularity of frozen fish. Many consumers now prefer to order frozen fish online, taking advantage of home delivery services that offer temperature-controlled packaging to ensure product quality. This trend is particularly evident in markets like North America and Europe, where online grocery platforms have gained widespread adoption.
6.3 Sustainability Concerns: A Shift Toward Eco-Friendly Choices
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they are increasingly seeking out sustainable seafood options. Frozen fish products that carry sustainability certifications, such as MSC or ASC labels, are gaining popularity among eco-conscious consumers who want to make ethical choices when it comes to their food purchases.
The frozen fish market has responded to this demand by prioritizing sustainable sourcing practices and promoting responsible fishing methods. Companies that demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship are seeing increased consumer loyalty and brand recognition.
In addition to sustainability, the frozen fish market is also focusing on reducing its carbon footprint by investing in energy-efficient freezing technologies and sustainable packaging solutions. These efforts align with the growing consumer demand for products that minimize environmental impact.
7. Challenges and Future Outlook
7.1 Cold Chain Management: A Critical Challenge
One of the biggest challenges facing the frozen fish market is the need for effective cold chain management. Maintaining the integrity of the cold chain—from the moment the fish is caught to its arrival at the consumer’s door—is crucial for preserving product quality and safety.
Any break in the cold chain can lead to temperature fluctuations, which can cause the fish to spoil or lose its nutritional value. This is a particular concern in regions with underdeveloped infrastructure, where reliable refrigeration and transportation systems may not be readily available.
To address this challenge, the frozen fish industry is investing in advanced refrigeration technologies and temperature monitoring systems that ensure the cold chain remains intact throughout the supply chain. These innovations are helping to reduce the risk of spoilage and improve the overall quality of frozen fish products.
7.2 Competition from Fresh Fish
Despite the advancements in freezing technology, the frozen fish market still faces competition from fresh fish. Many consumers continue to perceive fresh fish as superior in terms of taste and quality, which can make it difficult for frozen fish to compete in certain segments of the market.
However, consumer education and awareness campaigns are helping to shift these perceptions. By highlighting the benefits of frozen fish—such as its convenience, longer shelf life, and comparable quality to fresh fish—industry stakeholders are working to change the narrative around frozen seafood.
7.3 Future Growth Prospects
Looking ahead, the frozen fish market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by several key factors:
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing innovations in freezing technology, packaging, and cold chain management will further improve the quality and accessibility of frozen fish products, making them more appealing to a wider audience.
- Sustainability Initiatives: The industry’s focus on sustainability and responsible sourcing will continue to attract eco-conscious consumers, who prioritize ethical food choices and seek out certified seafood products.
- Emerging Markets: The expansion of cold storage infrastructure in emerging markets, such as Latin America, Africa, and Asia-Pacific, will open up new opportunities for growth. As frozen fish becomes more accessible in these regions, demand is expected to rise, driving further market expansion.
- Health and Wellness Trends: The global health and wellness trend will continue to fuel demand for nutrient-rich foods like fish. Frozen fish, with its convenience and health benefits, is well-positioned to capitalize on this trend.
Conclusion
The frozen fish revolution is reshaping the global fish processing market, offering consumers a convenient, nutritious, and sustainable alternative to fresh seafood. With advancements in freezing technology, growing consumer awareness of the health benefits of fish, and an increasing focus on sustainability, the frozen fish market is poised for continued growth in the years to come.
As the industry addresses challenges such as cold chain management and competition from fresh fish, it is clear that frozen fish will play an increasingly important role in meeting the world’s growing demand for seafood. Whether through technological innovations, eco-friendly practices, or the expansion of emerging markets, the frozen fish revolution is here to stay—reshaping how we consume, process, and think about seafood.