The Integration of STEM Education in Early Childhood Learning
Introduction to STEM Education
STEM education, which stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, is an interdisciplinary approach to learning where academic concepts are coupled with real-world lessons. In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven world, these fields have become increasingly pivotal. STEM education not only equips students with critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills but also fosters innovation and creativity. These competencies are essential as they contribute to advancements in various sectors, including healthcare, information technology, automotive, aerospace, and many others.
Emphasizing STEM from an early age is crucial as it lays the foundation for a child’s intellectual development. By nurturing an interest in these subjects during the formative years, educators and parents can inspire future generations to pursue careers that drive societal progress and economic growth. This early introduction can help demystify complex concepts, making them more accessible and engaging for young minds. Furthermore, integrating STEM into core curriculums encourages collaboration, fueling a collective approach to tackling real-world problems.
In the modern educational landscape, STEM initiatives aim to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. They provide students with hands-on experiences, encouraging an experimental mindset where trial and error become integral parts of learning. By integrating STEM disciplines into early childhood education, students can cultivate a lifelong interest and proficiency in these critical areas. As technology continues to advance, proficiency in STEM subjects will remain indispensable, ensuring that future generations are equipped to meet new challenges head-on.
Early childhood education is a critical phase in a child’s development, encompassing the ages from birth to eight years old. During this time, children’s brains are highly adaptable and primed for learning, making it an optimal period for foundational skill-building. The significance of early childhood education cannot be overstated, as it lays the groundwork for cognitive and social development that will influence a child’s entire academic journey and beyond.
Cognitive Development
In the early years, children’s brains develop at an unparalleled rate. This period is marked by rapid neural development, where trillions of synapses are formed, creating pathways essential for cognitive functions. During early childhood education, children are introduced to basic concepts in language, mathematics, and problem-solving. These early interactions and experiences are vital as they shape the brain’s architecture, setting the stage for more complex skills and knowledge acquisition later in life.
Social Development
Equally important is the social development that occurs during early childhood. Through interactions with peers, educators, and their environment, children learn crucial social skills such as cooperation, communication, and empathy. These skills are foundational for forming relationships and navigating social environments, both of which are essential for later success in life. Structured early childhood education programs provide children with opportunities to develop these social competencies in a supportive and nurturing environment.
Building Foundational Skills
Foundational skills acquired during early childhood education serve as building blocks for future educational endeavors. Basic literacy and numeracy skills are often emphasized, but equally important are critical thinking, creativity, and curiosity. These foundational competencies are crucial for understanding and integrating STEM education later on. By establishing a robust foundation, children are better prepared to tackle increasingly complex subjects and think innovatively.
In conclusion, the importance of early childhood education in cognitive and social development cannot be understated. Early years are formative, offering the perfect window of opportunity to build essential skills. Therefore, integrating STEM education at an early age can leverage this developmental phase, enabling children to thrive educationally and socially.
Benefits of STEM Education for Young Children
STEM education, encompassing science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, offers a range of benefits for young children, significantly enhancing their cognitive and social development. One of the primary advantages of integrating STEM into early education is its ability to foster curiosity. Young minds exhibit an innate desire to understand the world around them. STEM activities, through hands-on experiments and exploration, provide a structured yet open-ended platform for children to ask questions, hypothesize, and seek answers, thereby nurturing their inquisitive nature.
Another substantial benefit is the enhancement of problem-solving skills. STEM education encourages children to engage with challenges critically and innovatively, guiding them through processes of trial and error. This iterative approach equips them with the ability to think logically and persistently, traits that are invaluable not only in academics but in everyday life. By working through real-world problems, children learn that failure is not a setback but a stepping stone to discovering viable solutions.
Creativity is another attribute significantly bolstered by an early introduction to STEM. Contrary to the misconception that STEM is purely analytical, it actually requires a great deal of creativity. Whether it’s designing a simple machine, coding a game, or conducting a scientific experiment, children are encouraged to think outside the box and innovate. This creative thinking, when nurtured from a young age, can lead to groundbreaking ideas and novel approaches to conventional problems.
Confidence building is a critical outcome of STEM education. As children master new concepts and skills, their confidence naturally increases. Successfully completing a STEM project or solving a challenging math problem boosts their self-esteem and reinforces a growth mindset. This sense of accomplishment and resilience lays the groundwork for a confident approach to future learning and problem-solving scenarios.
Moreover, the real-world applications of STEM are vast. Early exposure to STEM helps children understand how the concepts they learn are used in daily life and various professions. For instance, early programming lessons could lead to a burgeoning interest in computer science, or an elementary engineering project could inspire a future career in construction or mechanical engineering. Recognizing these practical applications not only enhances learning relevance but also broadens children’s horizons regarding potential career pathways in the ever-evolving job market.
Challenges in Integrating STEM in Early Childhood
Integrating STEM education into early childhood learning presents a variety of challenges that educators and parents must navigate. Firstly, there is a prominent issue pertaining to the lack of resources. Providing adequate materials and technology for effective STEM instruction can be financially burdensome for many educational institutions, particularly in underfunded areas. Access to high-quality, age-appropriate STEM tools is critical for fostering an engaging learning environment, yet these resources are often scarce.
Another significant challenge is the insufficient training and professional development for teachers. Educators may not feel adequately prepared to deliver STEM content, which typically encompasses specialized fields such as science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. This lack of confidence and knowledge can hinder effective instruction and deter educators from incorporating STEM activities into their curriculum. Comprehensive training programs are necessary to equip teachers with the skills and strategies needed to effectively teach STEM subjects to young learners.
Additionally, there are prevalent misconceptions about young children’s ability to comprehend complex STEM concepts. Some educators and parents might underestimate the capacity of early learners to engage in rigorous STEM activities, thereby limiting their exposure to these subjects. It is crucial to recognize that even at a tender age, children are capable of developing foundational skills in critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity through appropriately designed STEM activities. Dismissing young learners’ potential can impede their academic growth and interest in these fields.
Addressing these barriers requires a collaborative effort among educators, parents, policymakers, and community stakeholders to ensure that early childhood education incorporates and values STEM learning. By tackling the challenges associated with resource allocation, teacher training, and shifting perceptions about children’s abilities, we can pave the way for a more inclusive and effective approach to STEM education in early childhood settings.
Effective Strategies for Integrating STEM
Integrating STEM education in early childhood learning requires a multifaceted approach that engages young minds through practical, interactive, and innovative methods. Effective strategies for integrating STEM can transform the classroom environment and stimulate curiosity and creativity among children. One of the most impactful methods is the incorporation of hands-on activities. These activities, such as building simple machines with everyday materials or conducting basic science experiments, offer children the opportunity to explore and discover through direct manipulation and observation. This practical approach provides an experiential learning path that is both engaging and memorable.
Interactive lessons are another cornerstone of effective STEM integration. Lessons that incorporate storytelling, role-playing, and problem-solving scenarios make learning more relatable and exciting for young students. For example, math concepts can be taught through stories where characters face challenges that require counting or measuring to resolve. Interactive board games and group activities can also effectively teach teamwork and critical thinking skills, essential components of STEM education.
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern STEM education. Introducing tablets, educational software, and interactive whiteboards into the classroom can significantly enhance learning experiences. Digital tools not only captivate children’s attention but also offer endless possibilities for interactive learning. Simple coding applications and robotics kits designed for young learners encourage them to experiment with programming and engineering concepts, laying a solid foundation for future STEM proficiency.
Support for both parents and educators is crucial for the successful integration of STEM education. Workshops and professional development courses can equip teachers with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively implement STEM activities in their classrooms. Online resources, including interactive websites and apps, provide additional platforms for children to explore STEM concepts outside the traditional classroom setting. Parents can also engage in their children’s learning by utilizing these digital tools, ensuring a cohesive and continuous learning journey.

Apple iPad (10th Generation)
PlayShifu PLUGO 3 Compatible
Support Plugo STEM Wiz. Turn your tablet into an interactive chessboard! Use real figurines to drive games on screen.
BUY…..
Together, these strategies create a dynamic and inclusive educational environment where young learners can thrive and develop a lifelong interest in STEM subjects. Through hands-on activities, interactive lessons, and the strategic use of technology, STEM education can be seamlessly woven into the fabric of early childhood learning, equipping the next generation with essential skills and knowledge.
Case Studies and Success Stories
The introduction of STEM education in early childhood has garnered significant attention over recent years, with numerous educational settings documenting its positive impact. One notable success story comes from Bright Futures Kindergarten, where the integration of STEM principles in the daily curriculum has resulted in measurable outcomes. Teachers at Bright Futures adopted an inquiry-based approach, allowing children to explore concepts in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics through hands-on activities.
Ms. Johnson, a lead teacher at Bright Futures, shared an anecdote about a project where children constructed simple machines using everyday materials. Through this project, young students not only learned about basic engineering concepts but also developed critical thinking skills and teamwork. Parents reported their children demonstrating a newfound enthusiasm for solving problems and a better understanding of how things work in their environment.
Another significant success story is from The Innovation Academy, which implemented a robotics program for preschoolers. By introducing age-appropriate robotics kits, children learned basic programming concepts and improved their fine motor skills. Feedback from parents at The Innovation Academy has been overwhelmingly positive, highlighting enhanced cognitive abilities and increased confidence in tackling complex tasks.
Quantifiable achievements further underscore the benefits of STEM education at early stages. For instance, a study conducted at Little Scientists Preschool revealed a 20% increase in problem-solving aptitude among children engaged in STEM activities compared to those who were not. Similarly, reading and numeracy scores saw an uplift, indicating a holistic enhancement in learning capabilities when STEM was woven into the early childhood curriculum.
These success stories from diverse educational settings exemplify the transformative power of STEM education in fostering curiosity, resilience, and academic growth among young learners. They reinforce the significance of early exposure to STEM principles in setting a solid foundation for future learning and development.
The Role of Parents and Guardians
Parents and guardians play a crucial role in the integration of STEM education in early childhood learning. Their active involvement can significantly enhance a child’s understanding and interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Creating a STEM-friendly environment at home is paramount. Simple steps such as providing access to age-appropriate STEM toys, books, and digital resources can ignite curiosity and foster a love for learning.
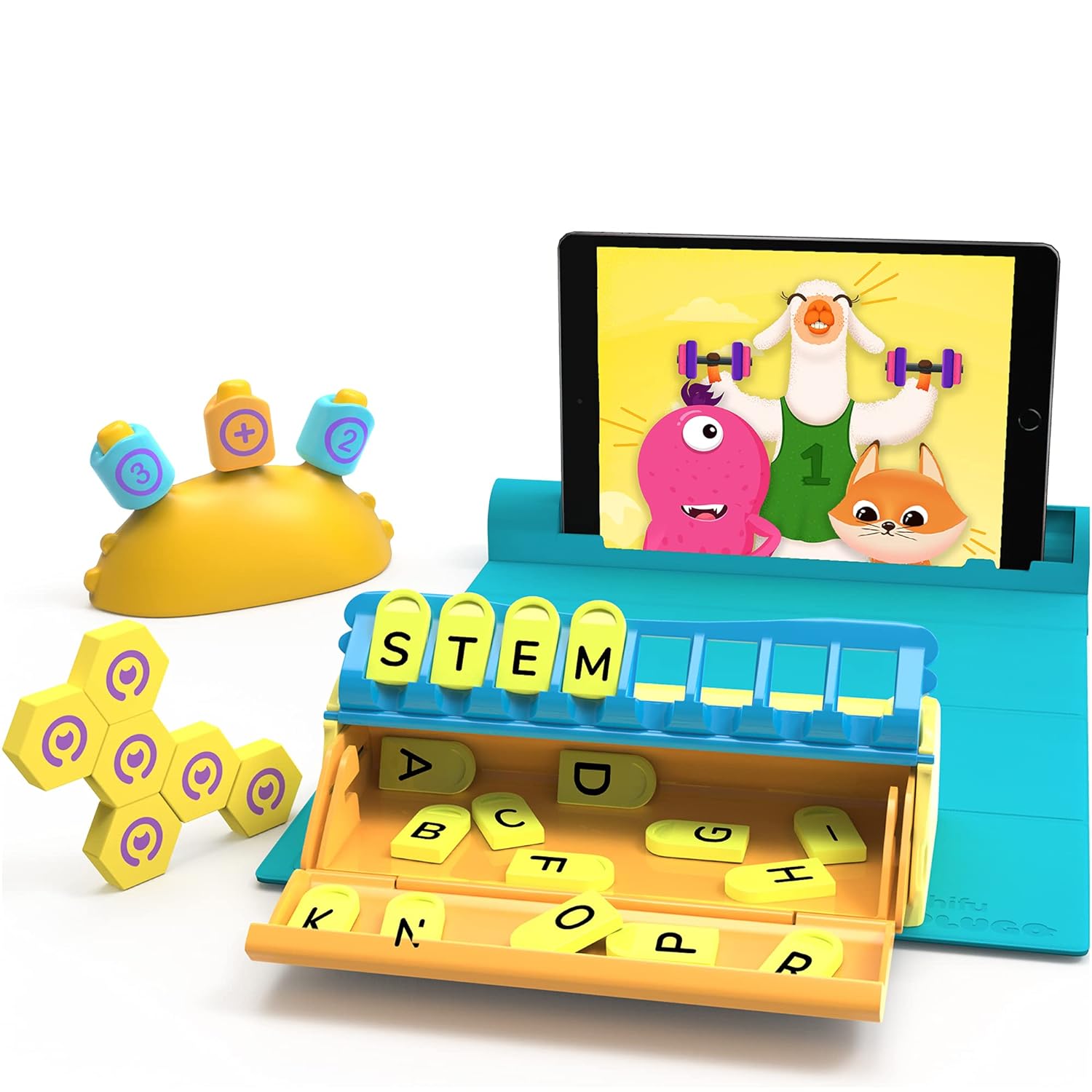

Early Childhood Learning
STEM KIT
PlayShifu PLUGO 3-in-1 pack combines the goodness of three AR-powered STEM kits – Plugo Count to learn math, Plugo Letters to spell and learn new words, and Plugo Link to solve puzzles with magnetic blocks. Hands-on learning and healthy screen-time guaranteed with story-based challenges. Watch the video to catch them all in action!
CHECK OUT…………For More Detail
Encouraging exploration and questioning is another essential aspect. Parents should inspire children to ask questions about the world around them and seek out answers together. This inquisitive mindset lays the foundation for scientific thinking and critical problem-solving skills. Engaging in discussions about everyday phenomena, such as the weather, cooking processes, or how household items work, can turn routine activities into valuable learning experiences.
Participation in STEM-related activities also plays a significant role. Parents can involve their children in DIY science experiments, building projects, or coding exercises. Local community science fairs, museums, and libraries often offer programs and resources designed to engage young minds in STEM subjects. Taking advantage of these opportunities provides practical experiences that reinforce classroom learning.
The importance of parental involvement cannot be overstated. By showing enthusiasm for STEM subjects, parents signal to their children that these fields are worth exploring and understanding. This positive reinforcement helps children develop confidence in their abilities and motivates them to pursue their interests further. Moreover, parents who actively participate in their child’s education can provide direct support, whether through assisting with homework or discussing new concepts introduced at school.
Ultimately, the integration of STEM education in early childhood learning is greatly enhanced by the role of parents and guardians. Their support, encouragement, and active participation pave the way for young learners to thrive in these critical disciplines. By making STEM a priority within the home, parents and guardians can cultivate a generation of thinkers, innovators, and problem solvers equipped for the future.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The integration of STEM education in early childhood learning is pivotal for the developmental and cognitive growth of young learners. By embedding Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics into early education, we can foster an environment that nurtures curiosity, promotes critical thinking, and builds foundational skills essential for future academic pursuits. This approach not only equips children with the necessary knowledge to thrive in a technologically advanced world but also encourages a lifelong love for learning and exploration.
Research has consistently shown that early exposure to STEM topics can significantly enhance a child’s problem-solving abilities and innovative thinking. Moreover, it cultivates essential skills such as collaboration, communication, and resilience, which are crucial in both academic and real-world settings. The long-term benefits of this early integration are profound, leading to improved academic performance, higher educational attainment, and greater career opportunities in STEM fields.
Looking ahead, there are several potential directions for future research and policy recommendations to further enhance STEM education in early childhood. Continued research is imperative to understand the most effective teaching methodologies and pedagogical frameworks that resonate with young learners. Furthermore, there is a need for comprehensive policy initiatives that support STEM curriculum development, provide professional development for educators, and ensure equitable access to STEM resources for all children, regardless of their socioeconomic background.
Advocacy efforts should focus on raising awareness about the importance of STEM education and fostering partnerships among educational institutions, industry stakeholders, and communities. These collaborations can drive innovation in teaching practices, provide funding and resources for STEM initiatives, and create a supportive ecosystem that champions early STEM education.
In conclusion, integrating STEM education in early childhood is not just an educational strategy; it is an investment in the future. By prioritizing STEM learning during these formative years, we are empowering the next generation with the skills and knowledge they need to navigate and succeed in an increasingly complex and technological world.