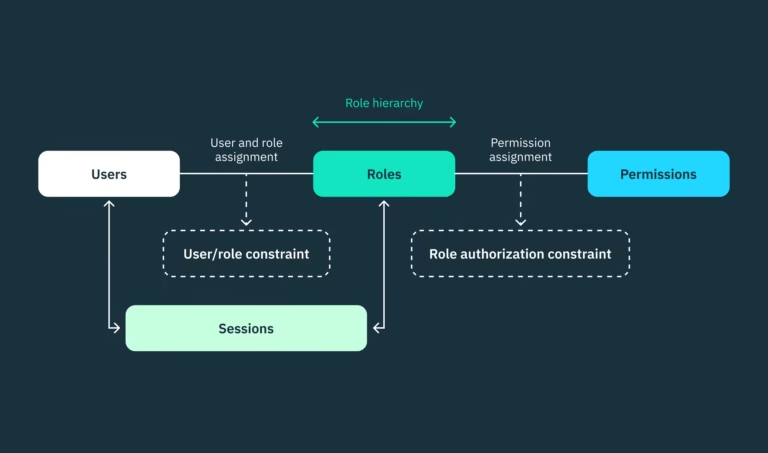
The Role of Automation in Enhancing Cybersecurity: In today’s digital world, the threat landscape is evolving at an unprecedented rate. Cybercriminals are using increasingly sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in systems, making it harder for organizations to stay ahead of threats. With the growing complexity and scale of cyber attacks, traditional manual methods of monitoring, detection, and response are no longer sufficient. This is where automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing cybersecurity.
Introduction to Cybersecurity and Automation
In an era where digital transformation is rapidly reshaping the business landscape, cybersecurity has emerged as a paramount concern for organizations worldwide. The importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated, as it protects sensitive data, maintains trust with clients, and ensures the continuity of operations. Cyber threats proliferate at an alarming rate, with malicious actors increasingly deploying sophisticated techniques to breach defenses. According to recent reports, organizations are facing a rising tide of cyber incidents, ranging from data breaches to ransomware attacks, which necessitate a robust cybersecurity framework.
Traditional manual methods of addressing these threats often fall short in effectiveness and efficiency. Security teams are frequently overwhelmed by the sheer volume of alerts generated by security systems, leading to alert fatigue and potentially missed critical incidents. Furthermore, the dynamic nature of cyber threats means that timely and precise responses are vital. Many organizations find themselves inadequately prepared to swiftly respond to evolving threats using manual processes, which can be both time-consuming and error-prone.
Recognizing these challenges, the role of automation in cybersecurity has become increasingly vital. Automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention, facilitating a quicker and more accurate response to security threats. By automating repetitive and labor-intensive processes, organizations can free up valuable resources and direct them towards more strategic initiatives. Automation empowers security teams to focus on high-priority tasks, such as threat hunting and incident analysis, thereby enhancing the overall security posture.
In summary, automation is not merely an enhancement but a necessary evolution in the cybersecurity domain. As threats continue to advance, leveraging automated solutions is essential for organizations striving to secure their digital assets effectively and efficiently. This blog post will delve deeper into how automation enhances cybersecurity, addressing its implications and best practices in the field.
Understanding Cyber Threats: A Growing Challenge
The digital landscape is fraught with various cyber threats that continue to evolve and pose a significant challenge to organizations across all sectors. Among the most prevalent types of threats is malware, which encompasses malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. These programs can range from viruses that replicate themselves to spyware that secretly gathers user data.
Phishing attacks, another major threat, involve the use of deceptive emails and websites to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers. These attacks have become increasingly sophisticated, often leveraging social engineering tactics to make their communications appear legitimate. Recognizing a phishing attempt has become a critical skill for employees in any organization, as falling prey to such tactics can lead to severe financial and reputational damages.

Additionally, ransomware has emerged as a particularly insidious type of cyber threat. This category of malware encrypts files on a victim’s system, effectively locking users out of their data and demanding a ransom for decryption. The consequences of ransomware attacks can be devastating, resulting in substantial financial losses and operational disruptions, especially for organizations that rely heavily on data availability. Moreover, data breaches, which occur when unauthorized parties gain access to confidential information, have become more frequent and severe. Breaches can lead to the exposure of personal data, potentially resulting in identity theft or further financial harm to victims.
Organizations of all sizes face unique challenges in combating these threats, as the rapid evolution of technology often outpaces security measures. As cybercriminals develop more sophisticated methods to bypass defenses, it becomes crucial for organizations to adopt advanced security strategies. Staying ahead of these persistent threats requires ongoing investment in cybersecurity measures, comprehensive training for employees, and the implementation of automated solutions that can respond to attacks in real-time.
What is Automation in Cybersecurity?
Automation in cybersecurity refers to the use of technology to perform tasks that would traditionally require human intervention, enhancing both efficiency and effectiveness in security processes. In this context, technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are pivotal. These tools analyze vast datasets to identify potential threats, streamline security responses, and reduce the burden on cybersecurity professionals.
There are different levels of automation in cybersecurity, ranging from basic automated tasks to sophisticated AI-driven security systems. At the most fundamental level, automation can be seen in tasks such as log management, where systems can automatically collect and analyze log data to identify anomalies. This basic level of automation helps organizations free up resources and improve response times, allowing human analysts to focus on more complex security concerns.
As we move towards more advanced levels, AI and ML can be leveraged to develop predictive models that anticipate potential threats based on historical data. These models can continuously learn and adapt, making them particularly effective in a rapidly evolving threat landscape. Furthermore, advanced automated incident response systems can react to threats in real-time, applying pre-defined protocols to mitigate risks before they escalate into significant breaches.
Incorporating automation into cybersecurity not only enhances security measures but also optimizes resource allocation within organizations. By automating routine security processes, businesses can achieve a more proactive security posture, ultimately minimizing their vulnerability to cyber threats. As organizations increasingly face complex and multifaceted cyber risks, understanding and implementing automation in cybersecurity becomes imperative for maintaining robust defenses.

Benefits of Automation in Cybersecurity
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, automation has emerged as a crucial component in enhancing cybersecurity. One of the primary benefits of automation is its capacity to drastically improve response times. Cyber threats can develop within seconds, and automated systems can identify, assess, and respond to these threats more swiftly than human teams. This increased speed is vital in mitigating potential damage and securing sensitive information before it becomes compromised.
Another significant advantage lies in the reduction of human error. Cybersecurity is a field where mistakes can have dire consequences, and automation serves to minimize the risk associated with manual operations. By employing automated solutions for repetitive tasks such as monitoring and alerting, organizations can ensure a level of consistency and reliability that human effort alone might not achieve. This reduction in human error not only bolsters security but also fosters a more efficient workflow.
Moreover, automation enhances threat detection capabilities. Machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence can analyze vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential threats. This proactive approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the threat landscape, enabling teams to stay ahead of potential attacks rather than reacting after the fact. Additionally, automated systems can process enormous data sets that would be impossible for human analysts to handle efficiently, allowing for better resource allocation.
Importantly, by integrating automation into their cybersecurity frameworks, organizations can free up human resources for more strategic and complex tasks. This redistribution of effort not only improves overall productivity but also allows skilled professionals to focus on developing security policies, conducting thorough risk assessments, and implementing advanced security measures that cannot be automated. As a result, the combination of automation and human expertise creates a more robust cybersecurity strategy.
Key Automation Tools and Technologies
Automation in cybersecurity refers to the use of technology to carry out tasks without the need for human intervention, allowing organizations to improve efficiency, accuracy, and speed in their security operations. Let’s dive deeper into the role automation plays in modern cybersecurity strategies.
1. Enhanced Threat Detection and Response
One of the most critical aspects of cybersecurity is the ability to detect threats in real-time and respond swiftly. Automation enables organizations to monitor vast amounts of data continuously and identify suspicious behavior, unusual traffic patterns, or any other signs of a potential attack.
By leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), automated systems can recognize patterns in both normal and malicious activities, making threat detection more efficient. Automation tools can flag these anomalies much faster than a human could, reducing the time it takes to respond to potential threats. This results in quicker decision-making and response times, significantly mitigating damage during a cyber attack.
Example: Automated intrusion detection systems (IDS) can analyze network traffic 24/7, flagging unusual behavior that may indicate a breach. Upon detection, an automated system can initiate an immediate response, such as isolating compromised segments or shutting down access to prevent further damage.
2. Reduction of Human Error
Human error remains one of the leading causes of security breaches. Whether it’s misconfigurations, missed alerts, or delays in responding to incidents, the manual handling of security tasks introduces the potential for mistakes.
Automation significantly reduces this risk by standardizing and streamlining processes. By automating repetitive and complex tasks such as patch management, malware scans, and log monitoring, organizations can reduce the likelihood of human errors. Automation ensures that these tasks are completed consistently, accurately, and without delay, helping maintain a stronger security posture.
Example: Automated patch management tools can identify vulnerabilities in software and systems, then deploy the necessary updates without needing human intervention. This minimizes the risk of overlooking critical updates that could lead to breaches.
3. Improved Efficiency and Scalability
Cybersecurity teams are often overwhelmed with the number of threats they need to monitor, the alerts they receive, and the manual tasks they need to perform. This challenge becomes even more difficult as organizations grow, and their networks expand in size and complexity.
Automation allows cybersecurity teams to scale their operations without hiring additional staff. By using automated tools to handle repetitive tasks such as log analysis, vulnerability scanning, and compliance checks, teams can focus on higher-priority tasks that require human expertise, such as threat hunting and strategic planning.
Example: Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems use automation to collect, analyze, and correlate logs from various sources in real-time. These systems can scale to monitor thousands of endpoints and systems simultaneously, making them invaluable for large organizations.
4. Proactive Threat Hunting
Rather than waiting for threats to manifest, automated cybersecurity tools enable a proactive approach to threat hunting. These tools use AI and machine learning to continuously scan for potential vulnerabilities, suspicious patterns, and emerging threats, even before they have a chance to impact the organization.
Automation-driven tools can conduct predictive analytics, assessing risks and suggesting preemptive actions to mitigate potential security risks. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of attackers by identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Example: AI-powered threat-hunting platforms can continuously monitor systems and networks for weak spots or unusual activity, allowing cybersecurity teams to prioritize areas that require immediate attention and minimize potential exposure.
5. Faster Incident Response and Mitigation
When a cyber attack occurs, the ability to respond quickly is essential to minimize damage. Automated systems can significantly speed up incident response by initiating pre-defined actions when a threat is detected. This can include isolating compromised systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or triggering alerts to the cybersecurity team.
Automation not only accelerates response times but also ensures consistency in handling incidents. Pre-programmed playbooks ensure that the same steps are followed every time, reducing the chances of oversights and ensuring that incidents are dealt with effectively.
Example: In the event of a ransomware attack, an automated system could immediately isolate the affected device, stop the encryption process, and alert the security team. This quick response could prevent the ransomware from spreading and limit the damage.
6. Automated Compliance and Reporting
Ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity. Automation can streamline the compliance process by conducting continuous audits, generating reports, and ensuring that security measures align with regulatory standards.
Automated tools can track changes in the network, flag non-compliant configurations, and generate the necessary reports for auditors. This reduces the burden on security teams and ensures that organizations remain compliant with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.

Example: Automated compliance tools can continuously monitor cloud environments, ensuring that all configurations meet regulatory requirements and alerting teams when any misconfigurations occur.
7. Incident Prioritization
In cybersecurity, not all threats are created equal. Some incidents may pose a minor risk, while others could lead to significant damage. Automated systems can help prioritize incidents based on the severity and impact of the threat, ensuring that the most critical issues are addressed first.
By automatically analyzing threat data and correlating it with potential impact, automation allows security teams to focus their efforts on high-priority threats, reducing the risk of significant breaches.
Example: A Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platform can analyze incoming alerts and rank them by severity, ensuring that the most pressing threats receive immediate attention while less critical issues are handled later.
Integrating Automation into Existing Security Frameworks
Integrating automation into existing cybersecurity frameworks requires a strategic approach that encompasses planning, execution, and monitoring. Organizations should begin by assessing their current security landscape to identify areas where automation can provide the greatest benefit. This may include automating repetitive tasks such as incident response, threat detection, or patch management. A thorough gap analysis should be performed to understand how automation can enhance existing processes and bolster the overall security posture.
Once the assessment is complete, organizations should develop a detailed integration plan that aligns automation initiatives with business objectives and compliance standards. This includes establishing clear goals for what the automation efforts seek to achieve, such as reducing response times or enhancing threat visibility. It is crucial that stakeholders across various departments are involved in the planning phase to ensure that the automation strategies address specific organizational needs and requirements.
During the execution phase, organizations should deploy automation tools in a controlled manner. This can involve piloting automation solutions in small, manageable environments before scaling them across the organization. Regular reviews and feedback loops are essential as they provide insights into the effectiveness and operational efficiency of the automation processes. Monitoring solutions should also be established to continuously evaluate the performance of automated systems, ensuring they meet security expectations and compliance mandates.
However, the integration process is not without challenges. Organizations must be cautious of common pitfalls such as over-automating or neglecting human oversight. Striking a balance between automation and manual intervention is vital in maintaining a robust security framework. By carefully planning and executing these integrations, organizations can significantly enhance their cybersecurity measures while aligning with their overarching business goals and compliance requirements.
Addressing the Challenges of Automation in Cybersecurity
While automation brings numerous benefits to the realm of cybersecurity, it also introduces significant challenges and risks that organizations must address. One key concern is the dependency that organizations may develop on automated systems. Over-reliance on these tools can lead to complacency among cybersecurity professionals, potentially diminishing critical thinking and the ability to respond effectively to threats when automation fails. It is essential for organizations to strike a balance between automation and human oversight to mitigate this risk.
Another challenge posed by automation in cybersecurity is the potential for false positives and false negatives. Automated systems are designed to detect threats and anomalies, but they are not infallible. False positives can lead to unnecessary alarm and wasted resources, while false negatives may allow genuine threats to infiltrate the system. Organizations must continuously fine-tune their automated tools and incorporate machine learning capabilities to improve accuracy and reduce these occurrences. Regular assessments and updates are critical to maintain the efficacy of automated security measures.
Additionally, the dynamic nature of cybersecurity threats necessitates ongoing updates and training for automated systems. Cyber threats evolve rapidly, and automated solutions must adapt in tandem to remain effective. This requires a sustained commitment to updating algorithms, integrating new threat intelligence, and providing training to staff on how to leverage these technologies effectively. Failing to adequately update automated systems may leave organizations vulnerable to emerging threats.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should engage in a comprehensive risk management strategy that emphasizes continuous monitoring, updates, and employee training. By fostering a culture that encourages collaboration between automated tools and human analysts, cybersecurity efforts can be fortified. Through careful management of both automation’s strengths and its inherent challenges, organizations can enhance their overall cybersecurity posture and resilience against an increasingly complex threat landscape.
The Future of Cybersecurity and Automation
The future of cybersecurity is inextricably linked to advancements in automation and emerging technologies. As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations are increasingly turning to automated solutions to bolster their defenses. Automated systems enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of cybersecurity measures, enabling rapid responses to potential breaches and threats. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) are at the forefront, allowing for real-time threat detection, vulnerability assessments, and predictive analytics. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate malicious activity, making it an indispensable tool in the cybersecurity arsenal.
Quantum computing is another transformative technology expected to impact cybersecurity significantly. Although still in its nascent stages, quantum computing holds the promise of solving complex problems that are currently beyond the reach of classical computers. This capability could revolutionize encryption methods, potentially rendering many existing security protocols obsolete. However, it also presents new challenges, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant algorithms to safeguard sensitive information against future threats. Thus, the landscape of cybersecurity will evolve with both opportunities and challenges presented by these advanced technologies.
As organizations increasingly embrace automation, it is crucial to address the role of human involvement in these systems. While automated solutions can handle repetitive tasks and enhance threat detection, human expertise remains vital in interpreting results, making informed decisions, and establishing security policies. The fusion of human judgment with automated processes can lead to more robust security frameworks. In the future, we can expect to see a collaborative approach, wherein cybersecurity professionals leverage automation to augment their capabilities while retaining oversight and accountability.
Conclusion: Embracing Automation for a Secure Future
As the digital landscape becomes increasingly complex, the role of automation in enhancing cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Throughout this discussion, we have explored various aspects of how automation technologies can significantly bolster an organization’s ability to defend against cyber threats. The integration of automated systems allows for more efficient detection and response to potential security incidents, addressing vulnerabilities that traditional methods may overlook.
Moreover, automated solutions empower cybersecurity teams by alleviating the burden of repetitive tasks. This not only enhances the efficiency of security operations but also allows professionals to focus on strategic initiatives that require human expertise. By harnessing automation, organizations can create a more proactive security posture that adapts to the evolving threat landscape.
Organizations are encouraged to adopt automation as a vital component of their cybersecurity strategies. Automated alerts, threat intelligence analysis, and incident response mechanisms can substantially reduce response times and minimize damages during a security breach. By embracing these advanced technologies, companies position themselves to stay ahead of potential cyber adversaries, thus ensuring the protection of their systems, data, and ultimately, their reputation.
In conclusion, the adoption of automation in cybersecurity not only mitigates risks but also fosters a culture of resilience within organizations. As cyber threats continue to grow in both sophistication and frequency, embracing automation is no longer a luxury but a necessity for organizations seeking to thrive in a secure digital environment. The future of cybersecurity lies in the collaboration of skilled professionals and innovative technologies, forming a robust defense against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.