
Introduction to Smart Cities and IoT
The advent of digital technology has led to the emergence of smart cities, a modern approach to urban planning and management that leverages the Internet of Things (IoT) to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable environments. Smart cities utilize interconnected devices and sensors to collect real-time data, enabling city administrators and residents to make informed decisions about various urban challenges. This evolution in urban design reflects a broader shift towards integrating technology into daily life, changing how cities operate and interact with their inhabitants.
At its core, the concept of smart cities revolves around improving the quality of life for citizens while optimizing resource management and energy consumption. IoT plays a pivotal role in achieving these objectives, offering innovative solutions that enhance urban infrastructure. For instance, smart traffic management systems utilize sensors and data analytics to monitor traffic flow, reducing congestion and enhancing mobility. Such systems not only improve travel times but also contribute to decreased pollution levels by minimizing idling and unnecessary stops.
Another significant application of IoT in smart cities is in waste management. Utilizing connected bins that can monitor fill levels allows for optimized collection routes, ensuring efficient use of resources and reducing operational costs. This not only provides economic benefits but also increases the sustainability of waste management practices.
Moreover, climate resilience in urban areas can be bolstered through IoT technologies. Smart environmental monitoring systems help detect and respond to pollution levels, urban heat islands, and other climate-related issues, facilitating proactive measures that protect public health and urban ecosystems. As we delve deeper into the various facets of smart cities, the profound impact of IoT on urban living becomes increasingly apparent, illuminating pathways toward a more integrated and intelligent urban future.
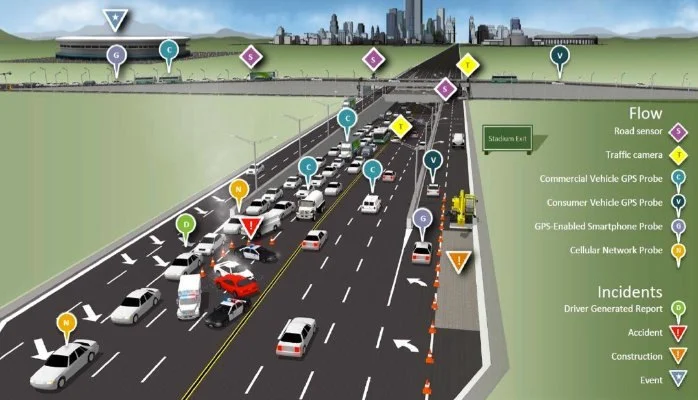
The Role of IoT in Traffic Management
The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) has significantly transformed the landscape of traffic management within urban environments. IoT technologies, such as sensors and traffic cameras, are increasingly employed to monitor and manage the flow of vehicles in real-time. This enables city planners and traffic authorities to gather high-quality data that drives informed decision-making. Smart traffic signals are one of the most prominent applications of IoT technology, allowing for adaptive control mechanisms that can respond dynamically to varying traffic conditions.
For instance, these traffic signals can adjust their timing based on real-time data collected from sensors embedded in the roadways. When traffic volume increases, the system can extend green light durations to minimize congestion, while during off-peak hours, it can shorten the cycles to enhance efficiency. Furthermore, the integration of IoT technology facilitates comprehensive data analysis, allowing authorities to identify patterns and predict traffic flows, which in turn leads to better infrastructure planning and resource allocation.
Additionally, adaptive traffic management systems leverage data analytics to improve safety and reduce delays. By using IoT devices, real-time updates can be disseminated to commuters through mobile applications or digital signage, informing them about alternative routes or unexpected road closures. Such proactive measures not only enhance daily commuting experiences but also contribute to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions, aligning with environmental sustainability goals.
Overall, the implementation of IoT in traffic management is paving the way for smarter, more efficient urban mobility solutions. As cities continue to grow and evolve, the role of IoT in ensuring seamless traffic flow and improved public safety will become even more critical, ultimately reshaping how residents navigate urban landscapes.
Enhancing Public Transportation with IoT
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into public transportation systems has revolutionized the way cities manage transit services. One of the most significant advancements is the implementation of GPS tracking in buses and trains, which provides real-time information on vehicle locations. This feature enables passengers to access accurate arrival times and enhances overall convenience, making commuting a less stressful experience. The capability to track vehicles not only improves service reliability but also allows operators to optimize routes and schedules based on actual demand and traffic conditions.
Moreover, mobile applications have become pivotal in enhancing user experience. These apps offer passengers instant access to valuable information such as delays, alternative routes, and available seating. By utilizing IoT data, the apps can provide personalized notifications and updates tailored to individual travel patterns, boosting user engagement and satisfaction. The ability to plan trips more effectively encourages higher ridership and fosters a culture of public transportation usage rather than relying solely on personal vehicles.
Smart ticketing solutions represent another innovative aspect of IoT in public transportation. These systems streamline the payment process through contactless fare systems, reducing the need for physical tickets and minimizing boarding times. Passengers can pay effortlessly through smartphones or transit cards equipped with RFID technology, promoting a smoother flow of people during peak hours. This ease of access not only caters to the modern consumer’s preference for digital transactions but also contributes to enhanced operational efficiency by reducing cash handling for transit authorities.
In summary, the incorporation of IoT technologies into public transportation systems is spearheading a transformation that markedly improves user experience. By offering real-time tracking, personalized mobile applications, and smart ticketing solutions, urban transit becomes more accessible and efficient, ultimately encouraging greater utilization of public transport while transforming the urban mobility landscape.
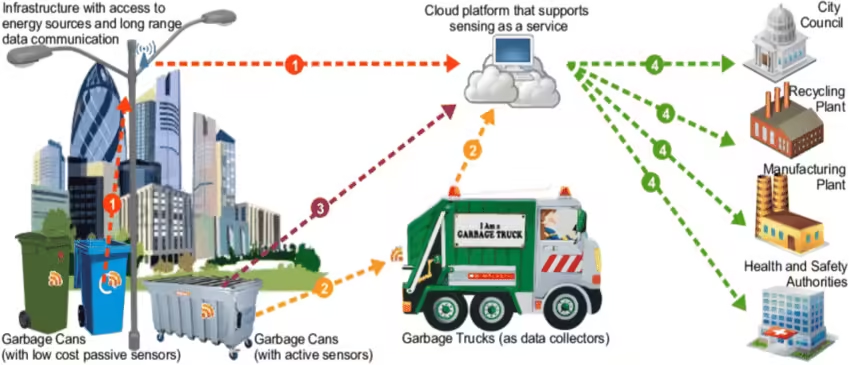
Smart Waste Management Solutions
In urban environments, managing waste effectively is a critical challenge, and the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology offers innovative solutions. Smart waste management employs IoT devices that not only enhance the efficiency of waste collection but also promote sustainable practices. One notable innovation in this realm is the deployment of smart bins equipped with advanced sensors. These sensors monitor waste levels in real-time, allowing city management to assess when bins need to be emptied. By utilizing this data, urban planners can significantly reduce unnecessary collection trips, thus optimizing route efficiency for garbage trucks while minimizing fuel consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, automated collection schedules emerge as a direct benefit of using IoT in waste management. Traditional waste collection schedules often operate on fixed routes and timelines, which can lead to inefficiencies, such as overflowing bins or premature collections. With the help of IoT analytics, cities can now adopt adaptive collection strategies. These strategies are informed by actual need, allowing for dynamic adjustment of collection routes based on current waste levels. As a result, cities not only save on operational costs but also enhance their capacity to maintain clean and healthy environments for residents.
The implementation of smart waste management systems also plays a significant role in promoting recycling initiatives. IoT devices can identify recyclable materials and track recycling rates, providing valuable insights into community participation. For instance, cities like San Francisco have successfully integrated smart bins that reward users for recycling, thereby fostering a culture of sustainability. Additionally, case studies from cities such as Barcelona highlight the transformative impact of these technologies, showcasing reduced landfill contributions and increased recycling. Overall, the fusion of IoT technology in waste management systems indicates a promising future for urban sustainability and efficiency.
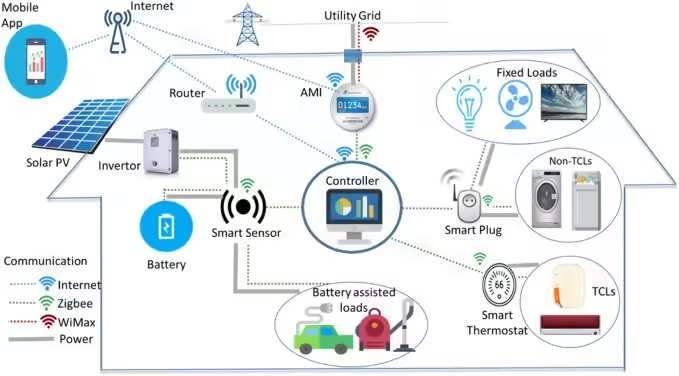
IoT in Energy Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative force in urban energy management, offering innovative solutions that enhance energy efficiency and promote sustainable practices. Smart grids represent one of the primary applications of IoT in this domain. These grids leverage advanced communication technologies to collect real-time data about energy consumption, enabling utility companies to optimize the distribution of electricity. By integrating IoT, utilities can respond swiftly to fluctuations in demand, thereby preventing outages and ensuring a stable supply of energy.
Another significant application involves smart meters, which allow consumers to monitor their energy usage closely. Unlike traditional meters, smart meters provide detailed insights into electrical consumption at any given moment. This technology empowers residents and businesses to make informed decisions regarding their energy consumption patterns, ultimately leading to more mindful usage. The data gleaned from these smart meters can also facilitate dynamic pricing models, enabling users to take advantage of lower rates during off-peak hours while contributing to grid stability.
Moreover, IoT-enabled energy management extends to the design and operation of energy-efficient buildings. Buildings equipped with IoT sensors can automatically adjust lighting, heating, and cooling systems based on occupancy and environmental conditions. Such automation not only enhances comfort but also significantly reduces energy waste. For instance, smart thermostats can learn user preferences and adjust heating or cooling settings accordingly, ensuring that energy is used only when necessary. This level of technological integration is instrumental in urban settings, as it contributes to lowering the overall carbon footprint.
In conclusion, the adoption of IoT technologies in energy management is paving the way for more efficient urban environments. By utilizing smart grids, smart meters, and energy-efficient building practices, cities can significantly enhance their energy management strategies, drive conservation efforts, and promote sustainability for future generations.
Improving Public Safety Through IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a pivotal tool in enhancing public safety within urban environments. By leveraging advanced connected technologies, cities can better monitor, respond to, and manage various safety-related challenges. One significant application lies in the deployment of connected surveillance cameras, which provide real-time monitoring of public spaces. These cameras employ video analytics to identify suspicious activities, allowing law enforcement agencies to respond promptly and effectively. For instance, certain cities have initiated smart camera networks that can automatically alert authorities when unusual behavior is detected, thus preventing potential crimes before they escalate.
In addition to surveillance, IoT facilitates the enhancement of emergency response systems. Advanced sensors can detect emergencies, such as fires or chemical spills, and automatically notify first responders. By utilizing location data and real-time assessments, these systems can significantly reduce response times. Notably, cities like San Francisco have implemented smart emergency alert systems that not only notify responders but also keep citizens informed through text messages and public announcements, ensuring that the community is aware of risks and can take protective measures promptly.
Moreover, environmental monitoring sensors represent another critical aspect of IoT’s contribution to public safety. These devices can track air quality, noise levels, and seismic activity, which in turn helps authorities address public health concerns and natural disasters. For example, cities prone to earthquakes use IoT-enabled seismic sensors that detect vibrations and send alerts to residents and emergency services, thereby providing crucial time for preparedness. The integration of these innovative technologies showcases how IoT can create safer urban spaces by proactively addressing potential threats, promoting awareness, and ensuring efficient response mechanisms. In conclusion, the transformative impact of IoT in enhancing public safety is evident through its diverse applications, illustrating its indispensable role in modern city life.

Data Privacy and Security Challenges
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies into urban environments presents significant data privacy and security concerns that must be addressed. As cities increasingly deploy connected devices, from smart traffic lights to waste management sensors, the volume of data generated raises questions about the safety of sensitive citizen information. These devices often collect a myriad of data, including location, personal habits, and public behavior patterns, which can be vulnerable to unauthorized access and breaches.
One of the primary challenges faced in managing IoT ecosystems is the sheer diversity of connected devices. Each device may have different security standards and protocols, leading to potential vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. For instance, an unsecured smart camera could inadvertently become a gateway for attackers, compromising the entire smart city infrastructure. Therefore, establishing a robust cybersecurity framework that ensures consistent protection across all devices is crucial in safeguarding urban data.
Moreover, protecting citizen data is paramount in maintaining public trust. Urban authorities need to transparently communicate how data is collected, processed, and stored. Engaging with residents to educate them on privacy protocols not only enhances collective awareness but also provides valuable feedback on community concerns regarding data handling. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA is an essential aspect of addressing these worries, as these laws provide guidelines for the ethical use of personal information.
To mitigate risks associated with data breaches, several potential solutions should be considered. This includes implementing strong encryption methods, ensuring device authentication, and regular software updates to address discovered vulnerabilities. Moreover, cities could establish strict guidelines and best practices for IoT manufacturers, promoting the development of secure devices. By proactively addressing these data privacy and security challenges, urban centers can harness the benefits of IoT while protecting their residents.
The Future of IoT in Urban Development
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a pivotal element in the future of urban development, marking a significant transition towards smart cities. Emerging trends exhibit that the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with IoT technology presents immense opportunities for enhancing urban planning. By leveraging AI, cities can utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets generated by IoT devices, enabling predictive analytics that enhance decision-making processes. This incorporation of advanced technologies is instrumental in understanding urban dynamics, predicting traffic patterns, optimizing public transport schedules, and managing resources more effectively.
Another vital aspect of IoT’s influence in urban development is its potential to foster sustainable growth. The integration of IoT solutions can significantly contribute to environmental sustainability through optimized waste management and energy efficiency. For instance, smart waste management systems, equipped with sensors, can monitor waste levels in real-time, allowing for efficient collection routes that reduce carbon emissions and improve operational efficiency. Similarly, smart grids that utilize IoT can manage electricity consumption by monitoring usage patterns and facilitating integration with renewable energy sources. These advanced systems not only decrease operational costs but also support cities in meeting sustainability targets.
Worldwide, innovative projects are demonstrating the beneficial impacts of IoT in urban environments. Initiatives such as smart traffic management systems in cities like Barcelona and Singapore are pivotal examples where IoT technologies have been deployed to streamline vehicular flow and reduce congestion. These forward-thinking projects showcase the potential for IoT in enhancing urban mobility and improving overall quality of life for residents. As cities continue to evolve, the synergy between IoT, AI, and machine learning is set to redefine urban development paradigms, paving the way for smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable urban living.
Conclusion: The Path to Sustainable Urban Futures
In examining the pivotal role of the Internet of Things (IoT) in reshaping urban environments, it becomes evident that these technologies are not merely enhancements to existing systems, but rather foundational elements that drive sustainability and efficiency in city life. Cities around the globe face multifaceted challenges, ranging from traffic congestion and energy management to waste disposal and public safety. IoT solutions pave the way for data-driven approaches that allow city administrators to optimize resource allocation and enhance the quality of life for residents.
The integration of IoT devices enables real-time monitoring and management, leading to improved traffic flow through smart traffic signals and dynamic routing systems that adapt to current conditions. Such advancements not only alleviate congestion but also minimize greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, waste management can be transformed with IoT-enabled bins that signal when they are full, ensuring that collection schedules are optimized, thereby reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Connected technologies foster community engagement, allowing residents to interact with their environment in new ways. For instance, applications powered by IoT can inform citizens about public transport availability, air quality, and energy consumption, promoting collective responsibility towards sustainable practices. Additionally, by leveraging big data analytics, cities can identify trends and respond to emerging needs proactively, making urban planning more responsive and resilient.
As we look toward the future, it is essential to emphasize the importance of continued investment in IoT infrastructure and research. The potential for innovation in urban management is immense, promising not only more efficient cities but also a significant reduction in environmental impacts. A collaborative approach involving governments, businesses, and citizens will be crucial in harnessing all that IoT has to offer, making strides toward achieving sustainable urban futures. Ultimately, the vision of smart cities relies on the principles of connectivity and adaptability, paving the way for an environmentally and socially responsible urban experience.






1 thought on “Transforming City Life: How IoT Manages Everything from Traffic to Waste”
Comments are closed.