
The Fragility of Peace
The ever-shifting landscape of international relations remains a poignant reminder of the fragility of peace. Throughout history, world wars have fundamentally reshaped nations, alliances, and the very fabric of societies. The catastrophic impacts of such global conflicts are indelibly etched in the annals of human history, illustrating how fragile peace can be amid escalating tensions and competing national interests. As we examine the repercussions of previous world wars, it becomes increasingly evident how quickly stability can dissolve into chaos and violence.
The world has witnessed numerous instances where the failure to maintain diplomatic dialogue and international cooperation has led to devastating conflicts. From the destructive roles of the First and Second World Wars to ongoing regional tensions today, these events have unleashed profound humanitarian and economic consequences. In some ways, the historical precedents set by these wars reveal the precarious nature of peace and underscore the potential for conflict to arise from seemingly minor geopolitical disputes. The continuous struggle for power among nations highlights the inherent vulnerabilities within the global system.
In the context of modern geopolitical dynamics, we must consider how emerging threats, such as cyber warfare and economic sanctions, might evoke a resurgence of global conflict. As nations grapple with issues like climate change, resource scarcity, and rising nationalism, the risk of escalating tensions increases. Furthermore, the interdependence of the global economy means that a localized conflict could have far-reaching repercussions that destabilize entire regions. This ongoing evolution in international relations serves as a crucial framework for understanding the implications of a potential return to a state of global war.
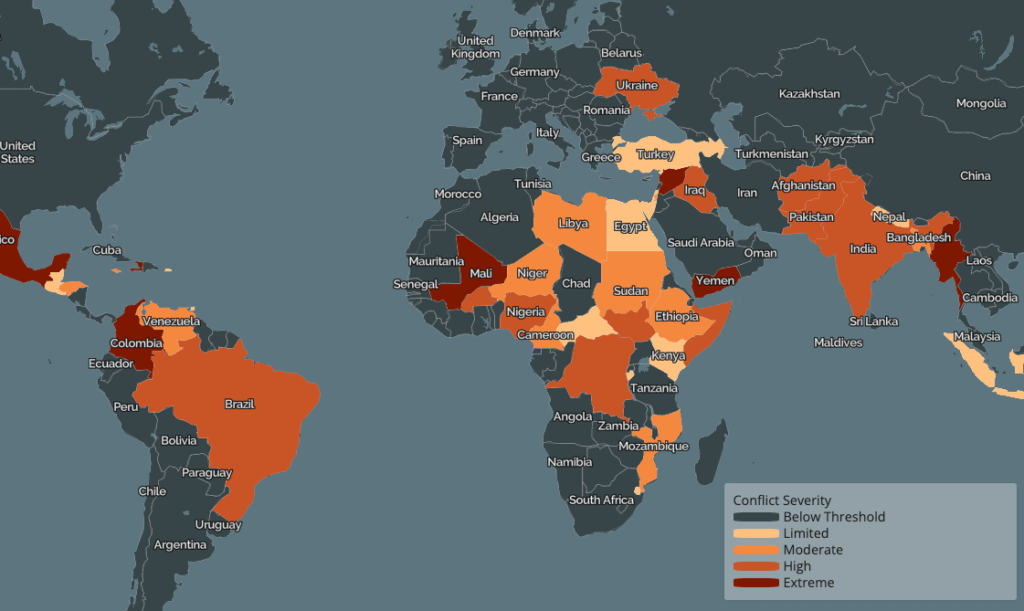
Historical Context: Lessons from the Past
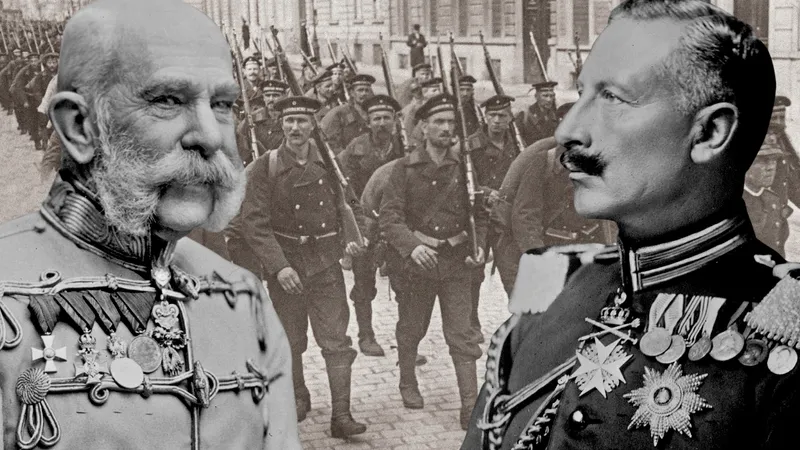
The 20th century was marked by two monumental global conflicts: World War I and World War II. Each war had distinct causes, involved a myriad of nations, and resulted in significant consequences that shaped the geopolitical landscape. Understanding these conflicts offers valuable lessons that could be applicable should similar circumstances arise in the future.
World War I, which lasted from 1914 to 1918, was primarily triggered by a complex web of alliances, militarism, and nationalism, culminating in the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary. Major participants included the Allies—comprised of nations like France, the United Kingdom, and Russia—and the Central Powers, led by Germany and Austria-Hungary. The war’s end resulted in the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed heavy reparations on Germany and redrew national borders in Europe. This post-war agreement is often cited as a precursor to World War II, emphasizing how decisions made during one conflict can lead to further unrest.
World War II, escalating from 1939 to 1945, had roots in unresolved tensions from the previous war. The rise of totalitarian regimes in Germany, Italy, and Japan showcased the failures of the peace settlements and economic instability of the interwar period. Key players included the Allies, such as the United States, the Soviet Union, and the United Kingdom, against the Axis powers. The implications of this war were profound; it led to the establishment of the United Nations and the beginning of the Cold War, significantly altering international relations.
Both wars illustrate the importance of diplomatic engagement and conflict resolution. Historical analysis underscores that understanding the past—the mistakes made and the lessons learned—can be instrumental in navigating modern global dynamics. By applying insights from these conflicts to current geopolitical tensions, nations may better prepare themselves to avoid repeating history’s gravest errors.

Societal Impact: Everyday Life in Wartime
In the event of a global conflict, the fabric of daily life would undergo profound transformations, impacting civilians in multifaceted ways. One of the most immediate changes would be the implementation of rationing, where essential goods such as food, clothing, and fuel become limited in availability. Families might find themselves relying on ration books to purchase these necessities, forcing them to prioritize their consumption and creatively substitute ingredients in their meals. As a result, the concept of grocery shopping would shift dramatically, embedding resourcefulness and community sharing into the everyday routines of households.
Moreover, propaganda would play a significant role in shaping public opinion and morale. Governments would likely deploy large-scale campaigns to rally support for military efforts, using various media outlets to disseminate messages that inspire patriotism and unity. This influx of information could create a polarized atmosphere, leading to heightened divisions within society. Individuals may feel pressured to conform to prevailing narratives, affecting personal relationships and community cohesion. The influence of propaganda might also extend to youth, as children could be encouraged to engage in war-related activities, further intertwining the concept of duty with daily life.
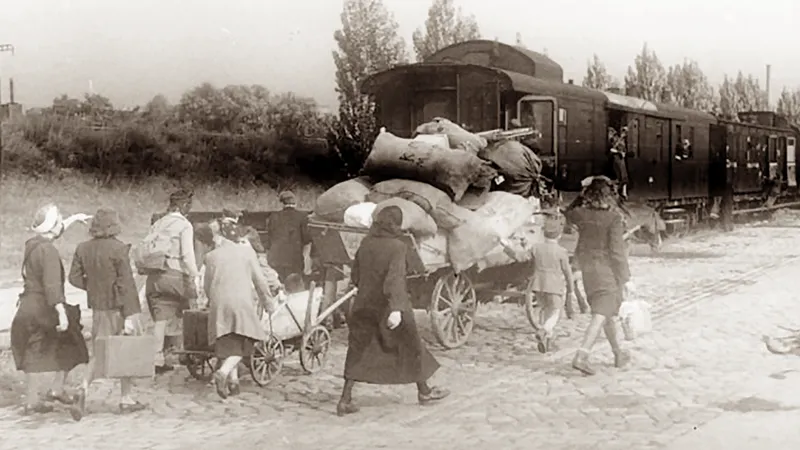
Displacement would be another harrowing aspect of civilian life in wartime. As conflicts escalate, individuals might be forced to leave their homes in search of safety, resulting in a significant refugee crisis. This change would not only disrupt the lives of those directly affected but also place immense pressure on host communities. Families would be faced with the challenges of adapting to new environments while grappling with the psychological toll of loss and uncertainty. The mental strain of living under constant threat, coupled with the societal upheaval caused by war, could lead to widespread anxiety and trauma, affecting generations to come.

Economic Consequences: The New Global Order
The resurgence of global warfare would undoubtedly reshape the economic landscape on an unprecedented scale. One of the most immediate implications would be a significant shift in trade patterns. Nations often redirect their trade relationships in response to conflict, seeking to secure resources and avoid regions that may become battlegrounds. We might observe a decline in interdependence as countries prioritize self-sufficiency, leading to a rise in domestic industries, particularly those focused on military and defense supplies. This could result in increased employment within military industries, while simultaneously driving traditional sectors into a downturn.
Economic sanctions would likely become a primary tool for nations engaged in war, targeting enemies through financial restrictions. These sanctions can disrupt supply chains and lead to increased costs for goods and services, further straining economies already teetering on the brink of recession. Historical precedents can be drawn from the post-World War II era, where countries employed sanctions not just to influence enemy behavior, but also as a means of asserting dominance in the new global order.
As economies grapple with the repercussions of global conflict, the potential for recessions becomes more pronounced. Job losses in affected industries may lead to heightened unemployment rates, creating a ripple effect that impacts consumers’ spending power and overall market stability. The construction of a new economic framework would become imperative in the face of such adversities. Governments may need to invest heavily in rebuilding efforts and reforming economic policies to adapt to the realities of war. Furthermore, international markets would experience volatility as uncertainties arise regarding future trade agreements and geopolitical stability.
Ultimately, the economic consequences of a return to global warfare would not only shape the immediate landscape but could also redefine the global order for generations to come, necessitating a recalibration of priorities for nations worldwide.

Political Landscape: Power Dynamics Revisited
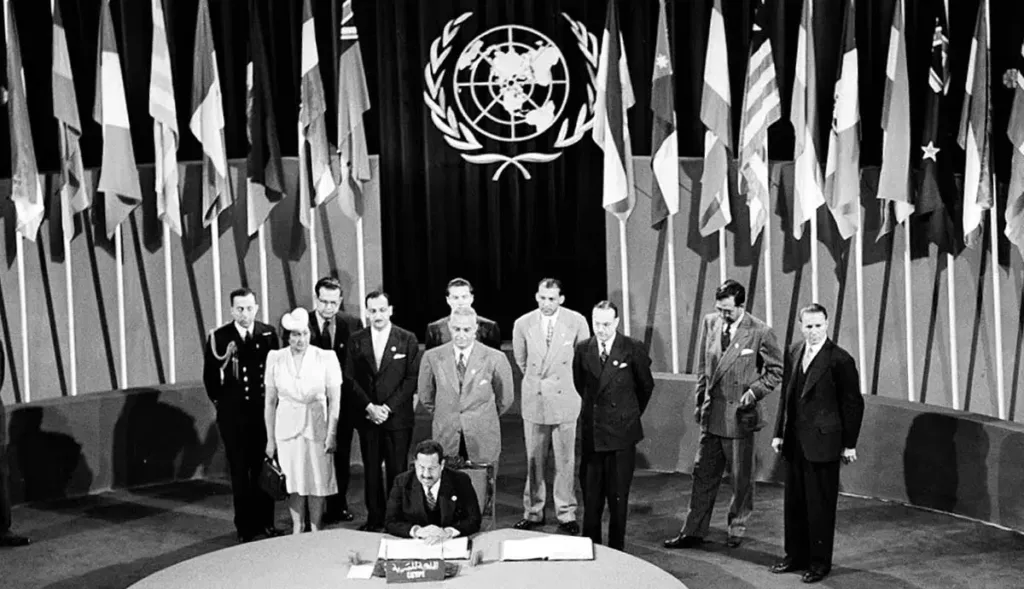
The potential resurgence of global conflict, reminiscent of the Great Wars, would inevitably reshape the political landscape in profound ways. As nations grapple with the ramifications of a new world war, existing alliances could be put to the test, leading to a realignment of power dynamics. Traditional superpowers—like the United States, Russia, and China—may find their influence challenged by emerging nations seeking to assert their presence on the global stage. These emergent actors could potentially disrupt the status quo, ushering in a new era characterized by shifted allegiances and transformative international relationships.
Amid this chaos, international organizations such as the United Nations could face existential challenges. Initially formed to promote peace and cooperation, these institutions may struggle to maintain efficacy when confronted with the exigencies of war. The potential for member states to bypass established frameworks in favor of unilateral actions could lead to fragmentation of global governance. Countries may prioritize nationalistic impulses over collaborative diplomacy, resulting in weakened multilateral agreements and a decline in collective resolutions to conflicts.
The rise of authoritarian regimes is another significant concern in this scenario. Historically, wartime conditions have facilitated the consolidation of power by leaders who may exploit national crises to undermine democratic institutions. Austerity measures and resource scarcity may propel populations toward leaders promising stability and security, often at the expense of civil liberties. If such trends materialize on a global scale, the principles of democracy and human rights could be severely jeopardized, fostering environments ripe for oppression.
Overall, the unpredictable nature of politics during wartime suggests that the landscape of power dynamics would undergo radical transformations. As nations engage in battles both militarily and ideologically, the implications for global order could be far-reaching. The outcomes of such conflicts remain uncertain, leaving the world to ponder the delicate balance between security and freedom in these tumultuous times.

Technological Advancements: Warfare and Innovation
In the contemporary landscape of warfare, the integration of advanced technologies has revolutionized combat dynamics and civilian experiences alike. One of the most significant advancements is the rise of cyber warfare, which allows nations to engage in conflicts without traditional military engagement. Cyber attacks can target critical infrastructure, steal sensitive data, or disrupt communication systems, thereby causing chaos and confusion in both military and civilian spheres.
Moreover, the development of drone technology has transformed the way warfare is conducted. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be deployed for surveillance, reconnaissance, and precision strikes, enabling military forces to engage targets from a safe distance. The ability to conduct operations without putting personnel at risk has not only changed combat strategies but also shifted the psychological landscape of warfare. Drones can operate invisibly in urban settings, blurring the lines between combatants and non-combatants, raising ethical questions about their use.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) also plays a pivotal role in modern warfare. AI-driven algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, improving decision-making processes and enhancing operational efficiency. This technology can be utilized for predictive analytics, allowing military strategists to anticipate enemy movements and shape their own tactical responses accordingly. Furthermore, AI weaponry, such as autonomous drones and robotic systems, poses new strategic challenges, raising concerns over accountability and the ethical implications of machines making life-and-death decisions.
As we examine these technological advancements, it becomes evident that their integration into warfare could profoundly impact civilian life during a prolonged global conflict. From the disruption of everyday activities to the transformation of cities into battlegrounds, the ramifications of advanced military technologies extend far beyond the battlefield. This interplay of innovation and warfare points to a future where technology not only shapes combat outcomes but alters the very fabric of society itself.
Humanitarian Crisis: The Refugee Experience
The onset of a global conflict invariably results in a significant humanitarian crisis, with one of the most devastating consequences being the rise in the number of refugees and displaced persons. Individuals and families are often forced to flee their homes as violence erupts, creating an urgent need for safety and a stable environment. The refugee experience is uniquely challenging, as it encompasses not only the physical act of escaping danger but also the complex and often perilous journey taken to seek asylum in a new land.
Upon fleeing their homeland, many refugees face numerous obstacles. The search for asylum is fraught with difficulties, including navigating bureaucratic procedures, securing essential documentation, and meeting stringent immigration requirements. Many are often not welcomed, facing hostility and xenophobia from host communities, which can exacerbate their sense of isolation during an already traumatic time. Access to basic survival necessities such as food, shelter, healthcare, and education becomes critically compromised for these individuals.
Moreover, the psychological toll of displacement is profound. Refugees commonly grapple with feelings of loss, grief, and anxiety, stemming from their abrupt separation from familiar surroundings and loved ones. The trauma associated with conflict, along with the challenges of starting anew in a foreign country, can lead to long-term mental health issues such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety disorders. These psychological scars, coupled with physical survival challenges, contribute to an overwhelming sense of despair for many displaced persons.
As international awareness grows regarding the plight of refugees, it is essential to advocate for comprehensive support systems that cater to the needs of these vulnerable populations. Understanding and addressing the multifaceted humanitarian crisis and the refugee experience can foster a compassionate response from nations, encouraging societies to provide the necessary aid and integration opportunities for those who have been uprooted by war.

Cultural Shifts: Art and Expression in Times of War
The impact of war on culture is profound, often resulting in significant transformations in artistic expression and creativity. During times of global conflict, art becomes a powerful vehicle for commentary, allowing artists to respond to the complex realities of warfare. Historically, literature, music, and visual arts have evolved as artists grappled with the chaos and destruction that accompany conflict. This section explores how war influences creative expression and highlights the essential role artists play as chroniclers of conflict.
Literature, in particular, has been shaped by the experiences of war. From the harrowing narratives of World War I poets who expressed the futility and horror of trench warfare to the contemplative prose of writers like Kurt Vonnegut, who offered critiques of society’s moral compass during times of conflict, literature provides a lens through which to understand the human condition in wartime. Novels such as “A Farewell to Arms” by Ernest Hemingway capture the emotional turmoil and loss, revealing the personal cost of global strife.
Music too serves as an expression of resilience and defiance during war. Wartime anthems and protest songs often resonate with soldiers and civilians alike, reflecting the sentiments of the era. Genres such as folk, rock, and hip-hop have been employed by artists to address and critique various aspects of conflict, from glorifying heroism to opposing militarism. Songs like Bob Dylan’s “Blowin’ in the Wind” invite listeners to consider the broader implications of war and advocate for peace.
Visual arts also surge during periods of conflict, with artists using their medium to convey powerful messages. Painters like Pablo Picasso, in works such as “Guernica,” have produced iconic representations of suffering and protest against war atrocities. Through their creative endeavors, artists not only process their experiences but also engage the public, raising awareness and prompting dialogue about the impacts of war.
In summary, art and expression evolve in response to war, acting as both a refuge for those suffering and a platform for critique. As we imagine a return to global conflict, understanding the historical interplay between war and culture helps us appreciate the vital contributions of artists in documenting and reflecting upon the human experience in turbulent times.

Conclusion: Preparing for an Uncertain Future
Reflecting on the potential outcomes of a return to world war, it becomes clear that the implications would extend far beyond the battlefield. Societal devastation, economic collapse, and the proliferation of humanitarian crises would undoubtedly characterize life during global conflict. Historical occurrences provide us with invaluable lessons about the fragility of peace and the necessity of resilience. Nations must grasp these historical narratives to comprehend the dire need for proactive measures in averting war.
In light of such potential outcomes, the importance of international cooperation cannot be overstated. Collaborative diplomatic efforts and sustained dialogue among nations stand as crucial pillars in building a more peaceful world. The global community must prioritize treaties, conflict resolution mechanisms, and mutual understanding to address the underlying causes of conflict before they escalate. Countries have a collective responsibility to foster environments conducive to dialogue instead of discord, thereby maintaining global stability.
Moreover, peacebuilding efforts should transcend mere policy-making. They should delve into the realms of cultural exchange, education, and shared economic initiatives. By investing in human development and promoting intercultural understanding, nations can cultivate a climate of peace that discourages aggression. History teaches us that isolated jurisdictions can lead to heightened tensions; thus, cross-national collaborations should be embraced enthusiastically.
In conclusion, as we imagine life under the specter of global conflict, it is imperative to remain vigilant and proactive in our pursuit of peace. The responsibility lies not just with governments but also with individuals and communities. To forge a future devoid of war, we must learn from the past and actively engage in peacebuilding initiatives, ensuring the creation of a stable, cooperative world for generations to come.






1 thought on “What If We Returned to World War? Imagining Life Under Global Conflict”
Comments are closed.